SFMC Query Studio Demystified: 5 Critical Use Cases
In the expansive digital marketing realm, data-driven strategies have emerged as the cornerstone of success. Within this landscape, Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio is a formidable tool, empowering marketers to unlock their data’s full potential.
Whether you’re a creative marketer seeking to tailor campaigns or a technical expert aiming to dive deep into data intricacies, this guide is tailored precisely for you. Prepare to delve into a world of expert tips, best practices, and techniques that will supercharge your marketing campaigns.
A Closer Look at Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio
Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio is a dynamic tool designed to run SQL queries directly on your Marketing Cloud data. What sets it apart from Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s traditional SQL environment is its user-friendly interface. It provides marketers with the capability to fetch, preview, and transform data in real-time, all within an interface resembling SQL Server Studio or MySQL Workbench.
Before we explore Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio, it’s essential to grasp the existing features and functionalities within Salesforce Marketing Cloud, as well as the limitations that come with these standard features. Understanding this context will underscore why solutions like Query Studio enhance your marketing campaigns significantly.
The Power of Salesforce Marketing Cloud
Salesforce Marketing Cloud (SFMC) is renowned for its robust suite of digital marketing tools designed to empower marketers in their data-driven endeavors. At its core, SFMC offers a range of features that allow users to interact with and manipulate data:
Data Extensions Filters: These are akin to tables in traditional databases, storing rows of data with defined columns. Marketers use them to segment and target their audience based on various attributes. Filtering data within these extensions is straightforward, with a user-friendly interface even newcomers can navigate.
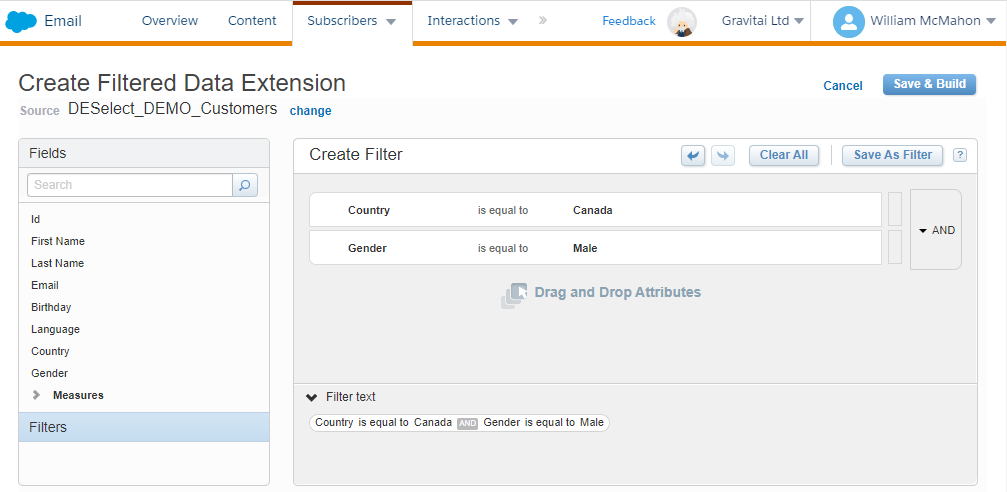
Basic SQL Query Functionality: SFMC provides a basic interface to run SQL queries for those familiar with SQL. This feature is handy for complex data manipulations extending beyond simple filtering. Marketers can extract, transform, and load (ETL) their data to suit specific campaign needs
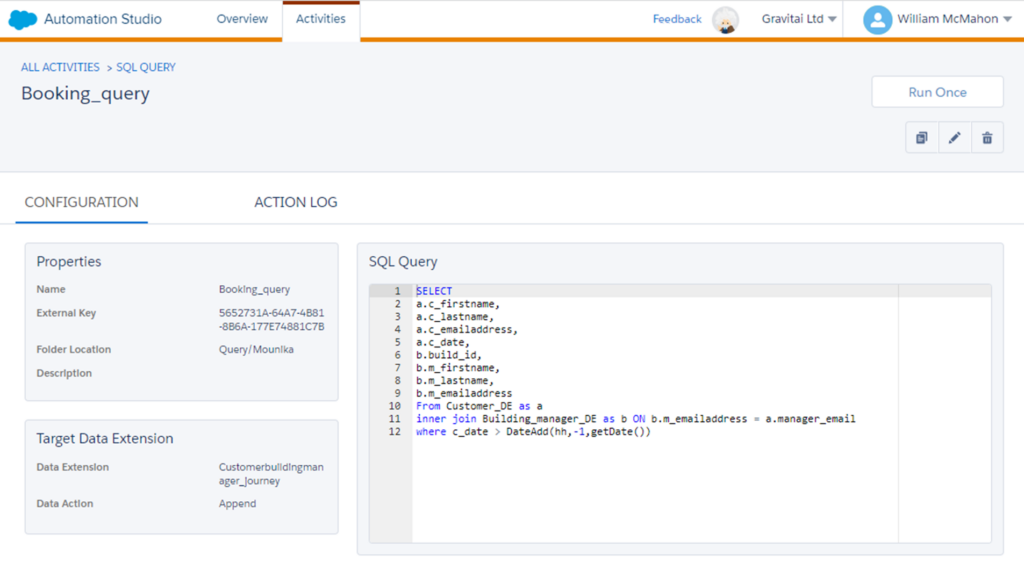
Automation Studio: This is where the magic of automation happens. Marketers can set up workflows to automate tasks like data imports, data filtering, and even running SQL queries at scheduled intervals.
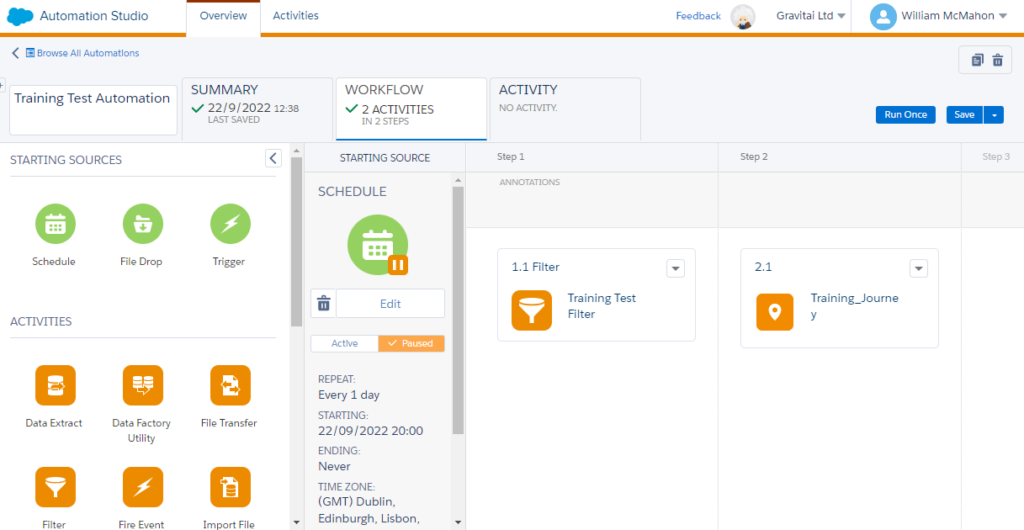
However, while these features are powerful, they come with their limitations:
- Single Data Extension Filtering: One significant limitation of Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s native capabilities is the restriction to filter within a single data extension at a time. Combining or comparing data across multiple data extensions is a challenge for the native tools, particularly when trying to gain a comprehensive view of customer interactions across different data sources.
- Performance of Filters: Filtering data within large data extensions can be sluggish, leading to delays in campaign launches or data analysis tasks. For marketers working in real-time or with tight schedules, these delays can impact the effectiveness and timeliness of their campaigns.
- Limitations in Joining Data: Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Data Extension Filters make it challenging to cross-join data extensions, hindering marketers from gaining a holistic view of their data.
- Complexity of Advanced Queries: While basic filtering and data manipulation are straightforward, creating advanced SQL queries requires a deeper understanding of the language, which can be a barrier for marketers without an SQL background.
- Lack of Real-time Result Viewing for SQL Queries: A significant constraint with Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s native SQL capabilities is the absence of real-time result previews. When an SQL query is executed, the output is directed and stored in a separate data extension instead of being immediately displayed for review. This fragmented approach can be cumbersome and time-consuming, particularly when iterative query adjustments are needed.
- Performance Issues: Running complex queries on large data extensions can lead to performance problems, including slow query execution or timeouts.
Given these limitations, there was a clear need in the digital marketing landscape for a solution that seamlessly combined user accessibility with sophisticated data manipulation. Enter Query Studio for Salesforce Marketing Cloud.
Query Studio: The Game-Changer
Query Studio isn’t just another tool in the marketer’s toolkit; it’s the linchpin that connects marketers to their data more intuitively and efficiently. Specifically crafted to address the challenges of real-time result viewing and multi-data extension filtering, Query Studio allows users to run SQL queries and instantly preview the results. This real-time feedback loop accelerates the data exploration, enabling marketers to make quicker, data-informed decisions.
Furthermore, Query Studio’s design inherently tackles the challenge of filtering across multiple data extensions, providing a more holistic view of customer data without cumbersome steps. By offering an environment that marries the simplicity of user-friendly interfaces with the power of advanced SQL capabilities, Query Studio is the beacon for those looking to elevate their data-driven marketing strategies.
Key Features & Benefits: Unveiling Query Studio’s Power
As we explore the world of Query Studio, it’s clear that this tool redefines how we engage with and comprehend our data within Salesforce Marketing Cloud. Let’s take a closer look at the essential features that make Query Studio an invaluable asset for tech-savvy marketers:
Interactive Querying: Gone are the days of navigating SQL queries in the dark. Query Studio empowers you to execute SQL commands and instantly witness the results. This real-time feedback accelerates your data exploration and cultivates a more intuitive grasp of your data manipulations.
Data Preview: Have you ever made a change and immediately wished you hadn’t? Query Studio’s data preview feature ensures you remain in control. Before committing to any alterations, you can preview the data, guaranteeing that your modifications align with your intentions. This not only reduces errors but also elevates data integrity.
Data Export: Data isn’t bound to a single platform. Query Studio simplifies data export, whether you want to share insights with a colleague or conduct further analysis using another tool. You can effortlessly export your results with just a few clicks, facilitating seamless cross-platform data utilization.
Syntax Highlighting: SQL, while powerful, can be intricate. Query Studio’s syntax highlighting feature enhances the readability of your SQL code by distinguishing commands, variables, and values using color codes. This makes the code easier to read and aids in swiftly identifying errors, ensuring smooth query execution.
Validation Tests: One of Query Studio’s standout features is its built-in validation tests. Before running a query, the platform conducts a series of checks to ensure the integrity and correctness of your SQL code. This proactive measure identifies potential errors or inconsistencies, enabling you to address them before execution. Not only does this save time by preventing erroneous outputs, but it also instills confidence, knowing that your queries are meticulously vetted for accuracy. In a realm where precision reigns supreme, this validation feature is a game-changer, ensuring your data manipulations are effective and error-free.
Reusable Templates: Efficiency takes center stage. Recognizing that many SQL queries are recurrent, Query Studio offers a feature to save frequently used queries as templates. This means you don’t have to rewrite or reconfigure a query you’ve employed before. Load the template, make the necessary adjustments, and you’re ready to roll, conserving time and effort.
Unlocking the Potential of Your Data
Data takes on diverse forms and structures in the vast ecosystem of Salesforce Marketing Cloud. At its core are Data Extensions akin to tables in traditional databases. They neatly store rows of data with defined columns, enabling marketers to segment and target their audience based on various attributes. However, the data landscape within Salesforce Marketing Cloud is more intricate than these extensions alone.
An often-underestimated gem lies in Data Views, which are system-generated, read-only tables offering a glimpse into the historical tracking data of your account. These tables capture crucial metrics such as email sends, opens, clicks, bounces, etc. Essentially, they unveil the backstage of subscriber engagement, enabling marketers to glean insights into past interactions and behaviors.
With Query Studio, marketers can seamlessly interact with Data Extensions and Views. This dual capability creates more comprehensive data exploration:
- Interacting with Data Extensions: When you launch a query in Query Studio, you’re instructing the platform to retrieve or modify data from these extensions. Moreover, leveraging the power of SQL, you can seamlessly join multiple data extensions, filter records, or even craft new calculated fields, enriching your data landscape and providing more nuanced insights for your campaigns.
- Tapping into Data Views: Query Studio’s ability to query Data Views opens up a world of analytical possibilities. Marketers can analyze historical engagement trends, segment subscribers based on past interactions, and forecast future behaviors. Marketers curate more informed and impactful campaigns by blending insights from Data Views with current data from Data Extensions.
In essence, Query Studio’s versatility in handling both Data Extensions and Data Views ensures that marketers attain a 360-degree view of their data, paving the way for more profound insights and data-driven decision-making.
The Foundation: Understanding SQL
Before delving into the practical applications and intricacies of SQL within Query Studio, let’s embark on a journey to grasp the fundamentals of SQL, or Structured Query Language.
What is SQL?
At its essence, SQL serves as a language that facilitates communication with databases. Think of it as the bridge connecting human queries with data-driven responses. Whether you seek to retrieve specific data, update values, or delete records, SQL equips you with the tools to achieve these tasks.
Basic SQL Operations:
- SELECT: This command retrieves data from a database. For instance, to view all records from a table named ‘Subscribers,’ you’d use: SELECT * FROM Subscribers;
- INSERT: It permits the addition of new records to a table. For instance, to add a new subscriber, you might use: INSERT INTO Subscribers (FirstName, LastName) VALUES (‘John’, ‘Doe’);
- UPDATE: This command modifies existing records. If you wish to change John Doe’s last name to ‘Smith,’ you’d use: UPDATE Subscribers SET LastName = ‘Smith’ WHERE FirstName = ‘John’;
- DELETE: It removes records from a table. To remove John Smith from ‘Subscribers,’ you’d execute: DELETE FROM Subscribers WHERE FirstName = ‘John’ AND LastName = ‘Smith’;
Understanding these foundational SQL operations lays the groundwork for harnessing the full potential of Query Studio within Salesforce Marketing Cloud.
Delving into SQL Joins:
SQL Joins are pivotal in merging data from multiple tables (or data extensions) based on related columns. They are essential tools in SQL, enabling you to create comprehensive datasets from fragmented information.
Table of Contents
Visual Representation
SQL Query
Description
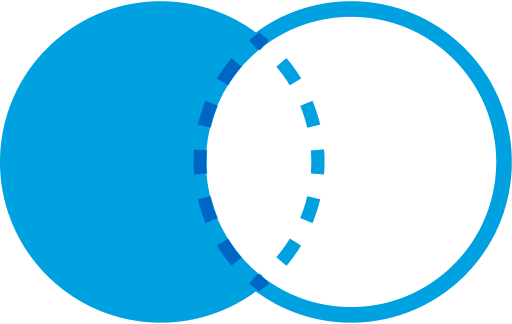
Select <Field List>
FROM DataExtensionA A
LEFT JOIN DataExtensionB B
ON A.Key = B.Key
Select <Field List>
FROM DataExtensionA A
LEFT JOIN DataExtensionB B
ON A.Key = B.Key
WHERE B.Key IS NULL
LEFT JOIN (or LEFT OUTER JOIN): These two options return all records from the left table, and the matched records from the right table. Unmatched records from the right table will appear as NULL.
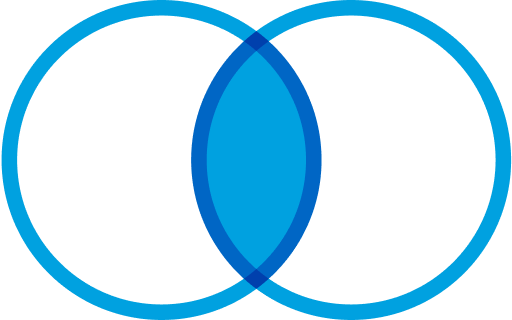
Select <Field List>
FROM DataExtensionA A
INNER JOIN DataExtensionB B
ON A.Key = B.Key
INNER JOIN: Fetches rows from both tables that satisfy the given condition. It focuses on the commonality between two tables.
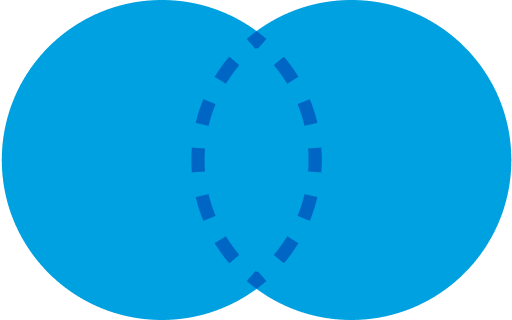

Select <Field List>
FROM DataExtensionA A
FULL OUTER JOIN DataExtensionB B
ON A.Key = B.Key
Select <Field List>
FROM DataExtensionA A
FULL OUTER JOIN DataExtensionB B
ON A.Key = B.Key
WHERE A.Key IS NULL OR B.Key IS NULL
FULL JOIN (or FULL OUTER JOIN): Combines the results of both LEFT and RIGHT joins. It returns all records when there’s a match in either the left or the right table.
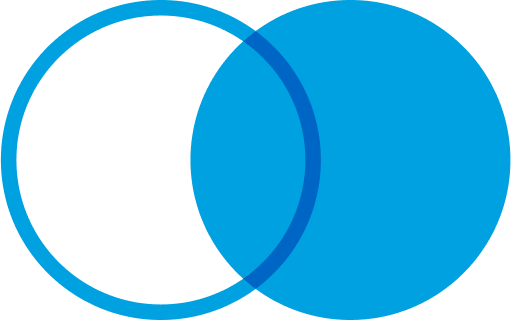
Select <Field List>
FROM DataExtensionA A
RIGHT JOIN DataExtensionB B
ON A.Key = B.Key
Select <Field List>
FROM DataExtensionA A
RIGHT JOIN DataExtensionB B
ON A.Key = B.Key
WHERE A.Key IS NULL
RIGHT JOIN (or RIGHT OUTER JOIN): Opposite of the LEFT JOIN. It returns all records from the right table, and the matched records from the left table.
As we venture deeper into SQL, it’s crucial to recognise that Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio introduces its own unique twists. While the fundamental principles of SQL remain intact, Query Studio deviates slightly from traditional SQL conventions. Here, what we traditionally regard as ‘databases’ are represented as data extensions or data views. Furthermore, operations like ‘INSERT,’ ‘UPDATE,’ and ‘DELETE,’ which are standard in traditional SQL, take on a different configuration within Query Studio.
When you save your SQL query within Salesforce Marketing Cloud, these operations are configured as settings. Additionally, SQL queries in Query Studio do not terminate with ‘;’ as in traditional SQL. Certain advanced commands/functions may also have restrictions but worry not – the validation messages in Query Studio are usually informative, guiding you through these differences.
As we delve further into this journey, you’ll become well-versed in navigating these distinctions, ensuring you can fully leverage Query Studio for your data-driven marketing initiatives.
Data Extensions: The Backbone of Your Data Structure
Data extension structures are pivotal in shaping how you interact with your audience data within Salesforce Marketing Cloud. While each organization may have unique data configurations, a typical data hierarchy emerges, which many Salesforce Marketing Cloud clients adopt. This hierarchy streamlines data management and lays the foundation for intricate data manipulations using tools like Query Studio.
Let’s explore this conceptual data hierarchy:
- In Salesforce Marketing Cloud, our Data Hierarchy is stored under Data Extensions, and a visual representation of the interconnectivity of each data extension can be visualized below.
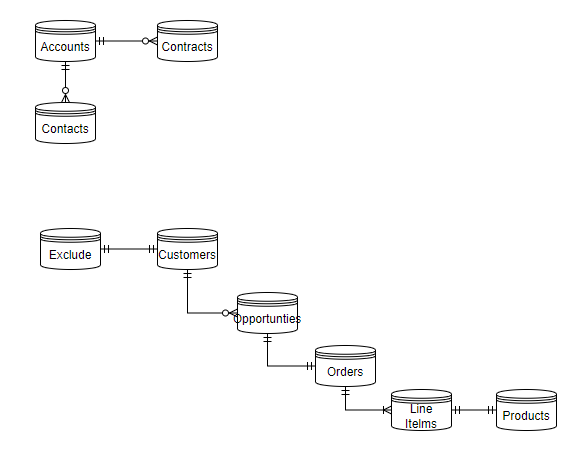
- Accounts: These form the backbone of any business data structure, representing the companies or entities you engage with, including partners, competitors, customers, or other stakeholders.
- Contacts: Individuals associated with these accounts, such as employees, representatives, or any person linked to an account.
- Contracts: Legal agreements between your company and these accounts detailing the terms of your business relationship.
- Customers: These are the individuals or entities purchasing your products or services, essentially the lifeblood of any business.
- Emails To Exclude: This is a critical data extension, particularly in email marketing, containing a list of contacts who have opted out or should not receive certain communications.
- Opportunities: These represent potential sales or deals, tracking the possibility of a contract or sale to a customer.
- Orders: Confirmed customer requests for products or services, signifying a successful opportunity conversion.
- Order Line Items: These provide granular details of each order, breaking down the products or services requested.
- Products: The items or services offered to customers, forming the core of what your business sells or provides.
While we won’t delve into the intricate configurations of each data extension and its fields, it’s essential to understand each entity’s relationship between data extensions. This understanding serves as a blueprint for how we join data and, more importantly, ensure we obtain the correct selection results.
With this understanding in place, we’re poised to demonstrate the capabilities of Query Studio. Using this typical data hierarchy, we’ll craft SQL queries to join, query, and build audience segments, showcasing the tool’s prowess in real-world scenarios.
Data Hygiene: Fuelling Your Marketing Machine
Just as a well-oiled machine operates at its best with clean fuel, your marketing strategies thrive on clean, accurate data. This is where the critical concept of data hygiene comes into play.
Understanding Data Hygiene: Data hygiene is the meticulous process of ensuring that a dataset is accurate but also consistent and usable. It involves identifying and rectifying errors, inconsistencies, and inaccuracies in data. In marketing, good data hygiene is akin to the compass guiding your campaigns to reach the right audience at the right time and with the right message.
The GDPR Perspective: Introducing regulations like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) has elevated data hygiene from a best practice to a legal obligation. GDPR mandates that organizations handle personal data carefully, emphasizing accuracy and relevance. Regular data cleansing is not just advisable; it’s essential to remain compliant, avoid substantial fines, and, most importantly, maintain the trust of your customers.
Query Studio: Your Data Cleansing Ally
Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio isn’t just a querying tool; it’s a potent instrument for data hygiene. Thanks to its robust SQL capabilities, you can:
- Identify and eradicate duplicate records
- Correct or transform data values
- Standardize data formats
- Validate and correct data types
For instance, if an email field contains values that don’t resemble email addresses or a date field has entries in multiple formats, these inconsistencies can be swiftly identified and rectified using SQL queries in Query Studio
The Crucial Role of Correct Data Types
Data isn’t merely about values; it’s about the context these values represent. An incorrect data type can distort this context. For instance, treating a numeric value as a text string can hinder mathematical operations. Ensuring that each field in your dataset has the correct data type is paramount for accurate analysis and operations.
In the world of data, there’s a fundamental principle: “The quality of your input determines the quality of your output.” This idea succinctly emphasises that the results you obtain are intricately linked to the quality of the data you start with. If your data is filled with mistakes, variations, or inaccuracies, these issues will ripple through all your marketing endeavours, potentially undermining their impact.
Use Case #1: COUNTing Records
In many scenarios, marketers require a quick overview of the volume of records within a specific data extension or the expected result from a SQL query. This snapshot allows you to gauge the size of a potential audience or data selection without running an entire data selection. Counting records provides vital insights into the data extension’s size and possible applications.
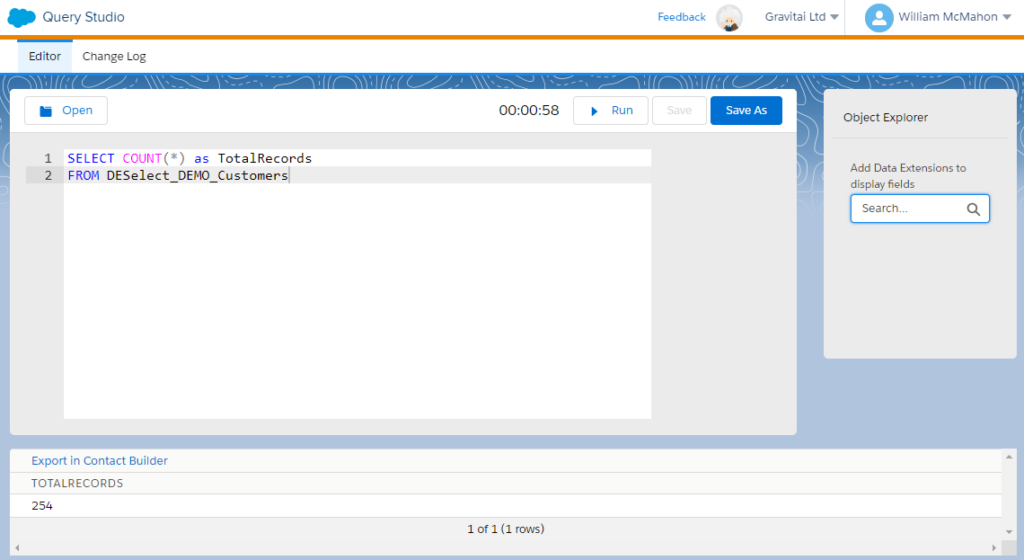
This SQL query returns a single value, ‘TotalRecords,’ representing the total number of records within the ‘Customers’ data extension. The same logic can be applied to any other data extension within your hierarchy to obtain a count of its records. It’s worth noting the aesthetics of Query Studio’s syntax colors and line numbers, which prove invaluable when validation errors occur, helping you quickly spot mistakes and typos.
Upon clicking the ‘Run’ button, Query Studio enters a processing queue on the Salesforce Marketing Cloud server. The processing time depends on various factors, including data volume and the time of day. Peak times may result in longer processing waits.
Use Case #2: WHERE Statement – Filtering our Data
In the world of data, precision is vital. Whether you’re homing in on a specific audience segment, dissecting product sales, or tracking account activities, the ability to filter data is indispensable. SQL’s WHERE statement is your precision instrument, enabling you to set conditions that filter and retrieve precisely the data you need from a data extension.
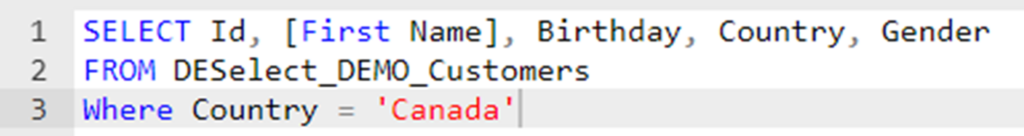
Building upon our previous example of counting records, let’s now put the WHERE statement to work by counting how many records exist in the ‘DESelect_DEMO_Customers’ data extension where the ‘Country’ field is ‘Canada’.
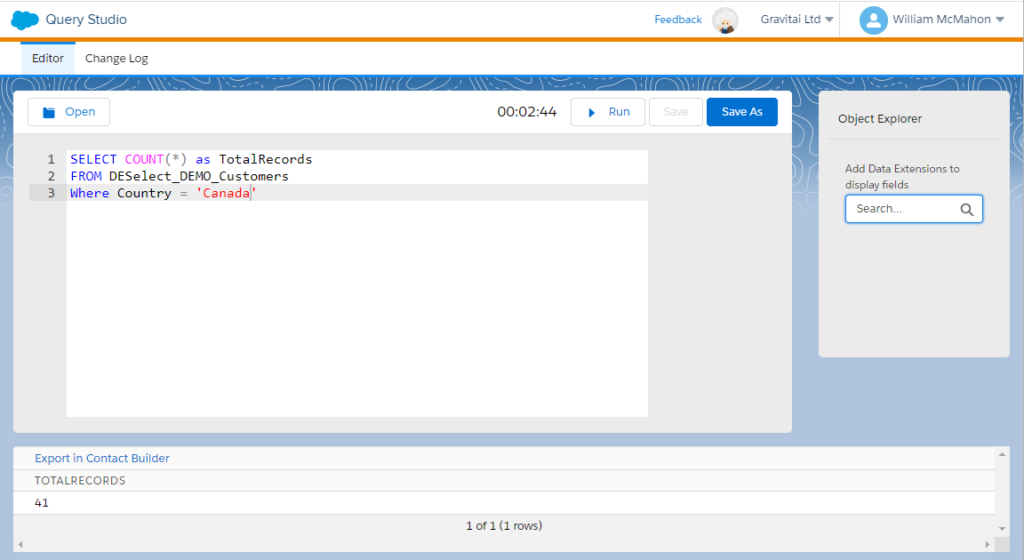
The WHERE clause, in SQL parlance, acts as the gatekeeper, allowing only records that meet specified conditions to pass through. These conditions can range from straightforward, like gathering all customers from a particular country, to more intricate, involving multiple criteria, such as country and gender.
As we delve deeper into SQL filtering, you’ll inevitably encounter scenarios where multiple conditions must be satisfied simultaneously, or any of several conditions will suffice. This is where the versatile AND and OR operators come into play:
AND Operator: This operator enters the scene when you need records that meet more than one condition, and all of these conditions must be true. For instance, if you’re in search of customers from Canada who are also male, both conditions must hold.
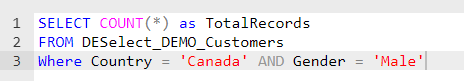
OR Operator: Conversely, the OR operator steps in when you filter based on multiple conditions, and it’s sufficient for any of these conditions to be true. For example, if you’re seeking customers from Canada or Ireland, satisfying either condition will fetch the record.
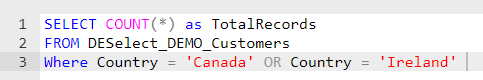
But a word of caution is in order here. Combining these operators requires deliberate care. Misusing or misordering them can lead to unintended results. For instance, without careful bracketing or logical sequencing, you might unwittingly retrieve records that don’t match your intended criteria.
For instance, imagine you’re trying to gather contacts from New York with an ‘Active’ status or contacts from Los Angeles, irrespective of their status. A poorly constructed query could net active contacts from cities other than New York, leading to data inaccuracies.
As a challenge and a learning opportunity, try to construct what the SQL query for this scenario would look like before reading on. If you’re grappling with the technical aspects of SQL, feel free. Keep your commitment to learning, as practice makes perfect. Stay tuned as we’ll discuss alternative tools that can simplify your data operations without a need for deep SQL knowledge.
The correct answer is:
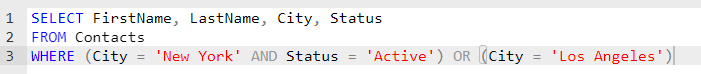
In this query, the thoughtful use of parentheses ensures that conditions are evaluated in the precise order needed to yield the desired results.
While the AND and OR operators are potent tools for refining your data queries, they should be handled with care. Proper structuring and a clear grasp of the logic you wish to implement are vital to ensure the accuracy of your results.
Use Case #3: FIELDS and Output
As we venture further into the world of SQL, it’s essential to grasp that numbers alone sometimes don’t paint the complete picture. The actual data within fields is often the key to understanding your audience or your business. Visualizing the data fields can unveil profound insights, whether you’re delving into customer demographics, scrutinizing product details, or dissecting account activities.
In Query Studio, making these data fields visible is a straightforward process. You can achieve this by adding the names of the data extension fields you wish to appear in the SELECT statement of your SQL query.
The selected results are then displayed in the output window, with records typically presented ten at a time for easier readability.
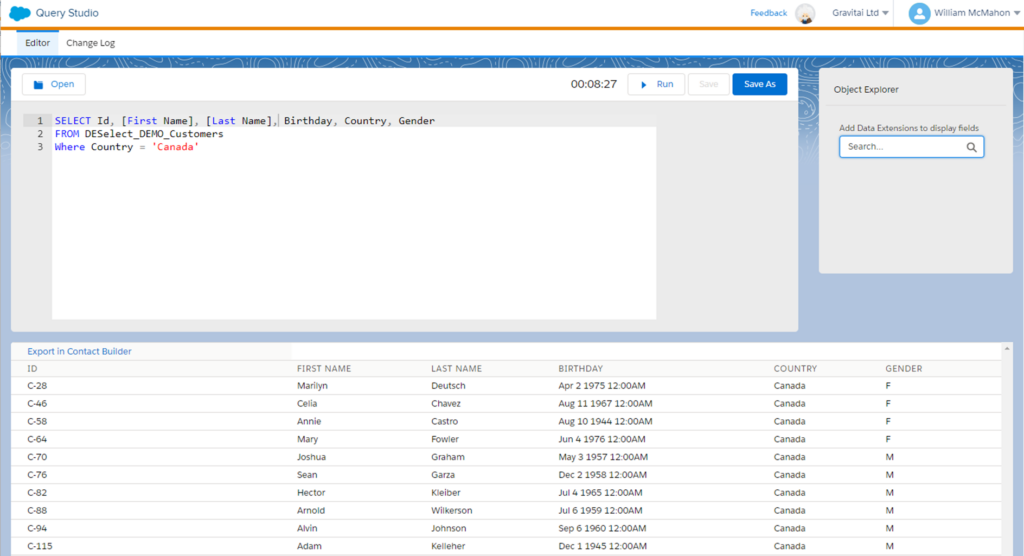
However, in Salesforce Marketing Cloud, field names sometimes contain spaces, reserved words, or special characters. While these naming conventions might be more human-readable, they can pose challenges during SQL querying. Additionally, there are situations where you might need to customize or transform the output, like combining fields or renaming them for clarity.
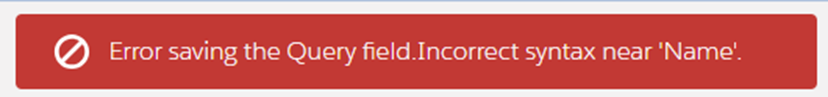
As shown earlier, dealing with field names containing spaces or special characters in SQL requires enclosing them in square brackets [ ] to ensure they’re recognized correctly. Furthermore, SQL provides the ability to rename (or alias) the output fields using the AS keyword. This is handy when you want the output to have a different name than the source field.
When saving the results of a query to a destination data extension in Salesforce Marketing Cloud, the destination data extension must contain fields with the same names specified in the query output. Mismatches between the output and destination fields can lead to errors or failed query executions.
You can also use SQL’s AS term when merging fields from your source data extension into a single output field. For example, you might want to concatenate [First Name] and [Last Name] into a single field called [Full Name]. The SQL query to achieve this is relatively straightforward.

This query takes the First Name and Last Name fields, combines them with a space in between, and outputs the result as Full Name.
Understanding these nuances in a platform like Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio can significantly enhance your data querying capabilities, allowing for more tailored and precise outputs that suit your needs.
Use Case #4: SAVE your Query and Results
Now that you’ve delved into crafting SQL queries in Query Studio, it’s time to explore how to save your queries. This step is essential if you intend to reuse your queries in Automation Studio for routine audience updates.
Saving your query is straightforward. Just click on the ‘Save As’ button and give your query a meaningful name. However, there are a couple of critical considerations when doing this.
First, you must select a destination data extension where you want to store the results. It’s essential to ensure that this data extension contains the fields or data schema you’ve specified in your SELECT statement. This alignment between your query’s output and the destination data extension is crucial for smooth execution.
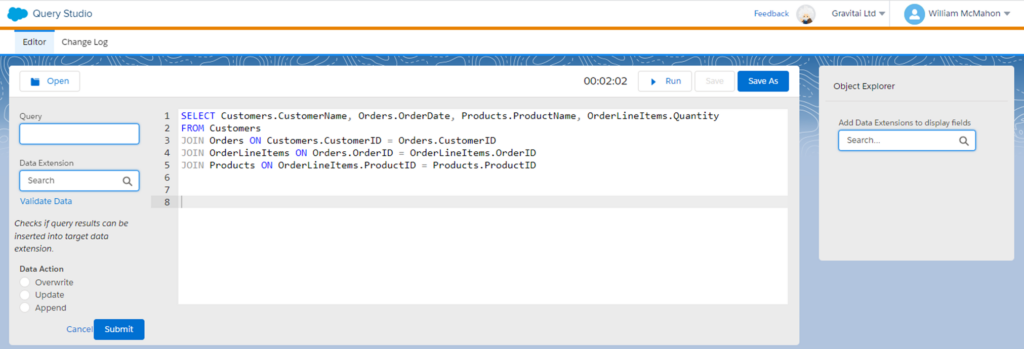
While there’s an ‘Export in Contact Builder’ feature that theoretically should create the data extension for you, it’s worth noting that it can sometimes be finicky. As a best practice, it’s often more reliable to manually create the data extension schema, ensuring it matches your query’s output.
After you’ve saved your query, you’ll also need to decide on the Data Action to take. This is a pivotal step that determines how the results of your query will interact with existing data. There are three distinct Data Actions to choose from: Overwrite, Update, and Append. Each action serves a specific purpose and can significantly impact your data.
Overwrite:
- Purpose: This action replaces the entire content of a target data extension with the results of your SQL query.
- Use Case: Consider a scenario where you have a monthly list of active subscribers, and at the beginning of each month, you want to refresh this list based on new activity. To achieve this, you can utilize the ‘Overwrite’ action. This action essentially swaps out the old data with the new data, guaranteeing that your list stays up-to-date and precise.
Update:
- Purpose: Instead of replacing all the data, the ‘Update’ action modifies only specific records in the target data extension based on the results of your SQL query.
- Use Case: Suppose you have a data extension of customers, and you’ve recently run a campaign where some customers updated their contact information. Instead of replacing the entire data extension, you’d use the ‘Update’ action to modify only those records with new information, leaving the rest untouched.
Append:
- Purpose: This action adds the results of your SQL query to the end of an existing data extension without altering the current records.
- Use Case: Imagine you have a data extension of newsletter subscribers, and after a recent event, you’ve gathered a new list of interested participants. Using the ‘Append’ action, you can add these new subscribers to your existing list without affecting the original subscribers.
Choosing the right Data Action is pivotal. An incorrect choice can lead to data loss, duplication, or inaccuracies. For instance, using ‘Overwrite’ when ‘Append’ was intended could erase valuable data. Conversely, appending data without checking for duplicates might lead to redundancy.
So, when saving your query and specifying the Data Action, consider the nature of your data and the intended outcome carefully. This decision ensures that your data remains accurate and aligns with your marketing objectives.
Use Case #5: DATEDIFF – Calculating time intervals between dates, plus Birthdays/Anniversaries
Whether you’re deciphering the time lapse between a customer’s initial interaction and their purchase, scrutinizing the timing of email dispatches, or commemorating your customer’s birthdays, the ability to compute date differences holds immense value. This is precisely where the DateDiff function in SQL steps in.
The DateDiff function is a potent tool for computing the disparity between two dates and presenting the outcome in the units you designate, such as days, months, or years. It proves incredibly useful when you aim to glean insights into customer behaviors or make data-driven choices grounded in time intervals.
However, there are some considerations to bear in mind. Firstly, the DateDiff function operates with ‘Date/Time’ fields, so maintaining consistent date formatting is imperative. Additionally, it necessitates three parameters in the correct sequence: the unit (e.g., day, month, or year), the commencement date, and the culmination date.
Let’s delve into an illustration. Picture this: you wish to ascertain how many days transpire between the placement of an order and its delivery. By computing the variance between the ‘Order Date’ and the ‘Delivery Date,’ you can acquire this data. This calculation serves to enlighten you on delivery durations and empowers you to apprise customers about any potential delays.
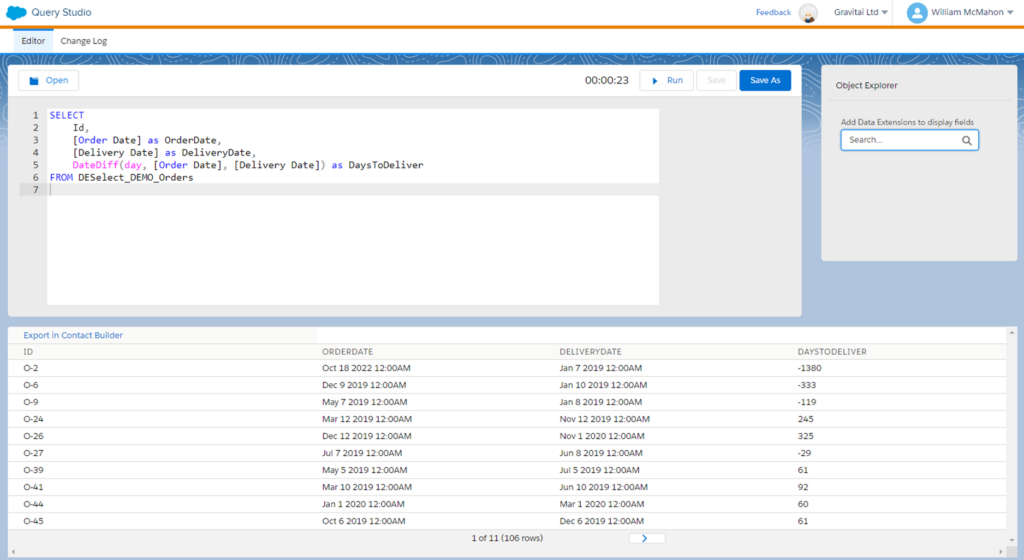
Now, let’s tackle a fun and practical scenario. How about identifying customers who are celebrating their birthday today? Sending personalized birthday greetings or offers is a fantastic way to engage with your customers and build loyalty. But here’s the twist – birthdays happen every year, and you don’t want to congratulate someone multiple times in a year!
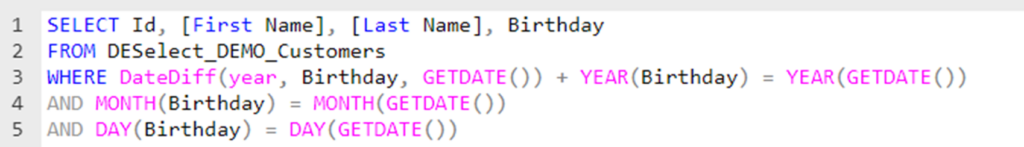
To do this, you’ll need to leverage the DateDiff function creatively. Instead of comparing the birthday field directly to today’s date, which includes the year, you’ll calculate the difference in years between the birthday and today. If this difference, when added to the birthday, equals today’s date (excluding the year), you’ve got a match.
In simpler terms, this condition helps you identify people who are celebrating their birthday today, regardless of which year they were born. It’s a smart way to handle anniversaries like birthdays.
You’ve got some handy date functions at your disposal in SQL. For instance, there’s GetDate(), which fetches the current date and time based on your system’s clock. It’s perfect for when you need the current timestamp.
In substitution to GetDate, there’s GetUTCDate(), and this one is particularly valuable for global applications. It provides the date and time in Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which remains consistent regardless of time zones or daylight-saving changes. This is essential when you want to work with a standardized time reference across different regions.
So, you see, SQL equips you with the tools to work with time and dates effectively, no matter where your data or users are located. Functions like YEAR(), MONTH(), and DAY() are also handy when you need to extract specific date components, like the year or month.
As you can see, we are starting to expand further our knowledge of SQL with some additional functions:
- GetDate() : This function returns the current date and time based on the system’s clock. When executed, this will return the current date and time, including hours, minutes, seconds, and milliseconds. It’s commonly used when you need to compare a date in your data to the current date and time.
- GetUTCDate() : Whilst not used in our Query above, it’s an important one to call out. Unlike GETDATE(), which returns the current date and time based on the system’s local settings, GETUTCDATE() provides a consistent time reference that isn’t influenced by time zones or daylight-saving changes. Therefore, we can use GetUTCDate() in substitution to GetDate() as it returns the current date and time based on the Coordinated Universal Time (UTC), which is essentially the world’s standard time reference.
- YEAR(), MONTH(), DAY() : These individual functions are particularly useful when you want to isolate or compare just a portion of a date e.g. Year, Month, Day.
As we’ve learned earlier, the WHERE function can be used be used to filter or match the results, and within the WHERE criteria we can also use DateDiff and other SQL functions.
In our example, The WHERE condition is checking if the sum of the difference in years between the Birthday and the current date (DateDiff(year, Birthday, GETDATE())) and the year of the Birthday (YEAR(Birthday)) is equal to the current year (YEAR(GETDATE())).
Using our example:
- Difference in years: 33
- Year of Birthday: 1990
- Sum: 33 + 1990 = 2023
- Current year: 2023
Likewise, the WHERE condition checks if the day and month of the Birthday field match today’s day and month, ensuring that only those celebrating their birthday today are retrieved.
The purpose of this condition is to identify records where the day and month of the Birthday match the current day and month, but without considering the year. This is a clever way to identify anniversaries, like birthdays, which occur on the same day and month every year but have a different year.
Let’s blow your mind even further – say you want to calculate the age of the customer and store it in the data extension. With the knowledge you’ve so far learned, how do you think you’d go about this?
It’s pretty simple, as you already have all of the code above, and you should be familiar with the AS function for renaming fields – remember?
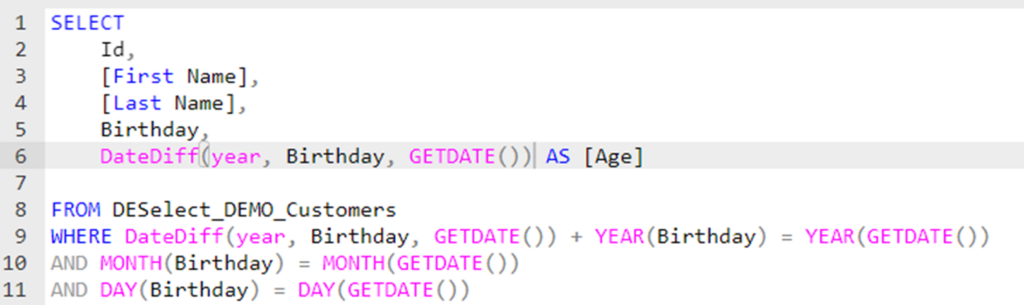
These date functions are fundamental tools in SQL, especially when working with date-time data. They allow for precise extraction and manipulation of specific components of dates, enabling detailed analyses and comparisons. In Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio, understanding and effectively using these functions can greatly enhance data querying capabilities, allowing for more tailored outputs and insights.
When combined, as seen in the birthday example, these functions can be used to craft complex conditions and criteria, ensuring that you can extract exactly the data you need, no matter how specific or nuanced your requirements might be.
A Quick Use Case Summary
Our journey into the world of SQL and Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio has been nothing short of fascinating. We’ve touched the surface of its vast potential through the examples and use cases explored here.
While these scenarios provide a solid foundation for your data-driven marketing endeavors, SQL, and Query Studio offer an ocean of possibilities. The depth and versatility of SQL, combined with the power of Query Studio, are limitless.
Limitations of Query Studio
While Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Query Studio offers valuable features for marketers, it’s crucial to understand its limitations to work effectively within its boundaries or explore alternative solutions when necessary. Let’s take a closer look at some important limitations to keep in mind:
- Query Length:
- Constraint: Queries in Query Studio have a character limit. Extremely lengthy or complex queries might not run or even fit within the tool.
- Implication: Query writers need to be concise and efficient in their query construction. If a query is too long, it may need to be broken down into multiple smaller queries or optimized for brevity. Here, it is necessary to know SQL well enough that you can make any necessary query, no matter how complex, in as few strings as possible.
- Execution Time:
- Constraint: There’s a maximum time limit (typically 30 minutes) for how long a query can run in Query Studio. If a query exceeds this, it will time out and fail to execute.
- Implication: This limitation can be challenging when working with large datasets or performing complex data manipulations. Users may need to optimize their queries for performance, break them down into more minor queries, or consider running them during off-peak times.
- Complex Joins:
- Constraint: While SQL allows for joining multiple tables or data extensions, doing so with large data extensions in Query Studio can be resource-intensive and slow.
- Implication: Joining multiple large data extensions can increase execution time (risking timeouts) and consume more resources, potentially affecting other processes. Users should strategically plan joins, ensuring they are necessary and optimized for performance.
- Error Feedback:
- Constraint: Query Studio might not always provide detailed error messages, making it challenging to pinpoint issues in a query.
- Implication: Debugging and troubleshooting can become time-consuming. Users may need to rely on their SQL knowledge or seek external resources to understand and resolve errors.
- Data Volume:
- Constraint: Query Studio is primarily designed for querying, not bulk data processing. It might not be the most efficient tool when dealing with millions of records.
- Implication: Users should consider other tools or platforms within Salesforce Marketing Cloud for extensive data processing tasks or break down tasks into more manageable chunks.
- Technical Language and Complexity:
- Constraint: SQL is a Programming Language, and Query Studio is just an SQL Query execution tool. Users require a steep learning curve to upskill on SQL, functions, and practices.
- Implication: The technicalities can become overwhelming for many non-developers, and mistakes can easily be made (e.g. selecting the wrong audiences).
Understanding these limitations is crucial for the efficient use of Query Studio. In some cases, users may find that more advanced tasks or working with extensive datasets are better suited for other tools or platforms within Salesforce Marketing Cloud or external data processing solutions.
Simplifying with DESelect
DESelect provides a valuable solution for marketers looking to simplify the process of data querying and manipulation in Salesforce Marketing Cloud. It bridges the gap between traditional marketing practices and the complexities of SQL, making data-driven marketing more accessible and efficient.
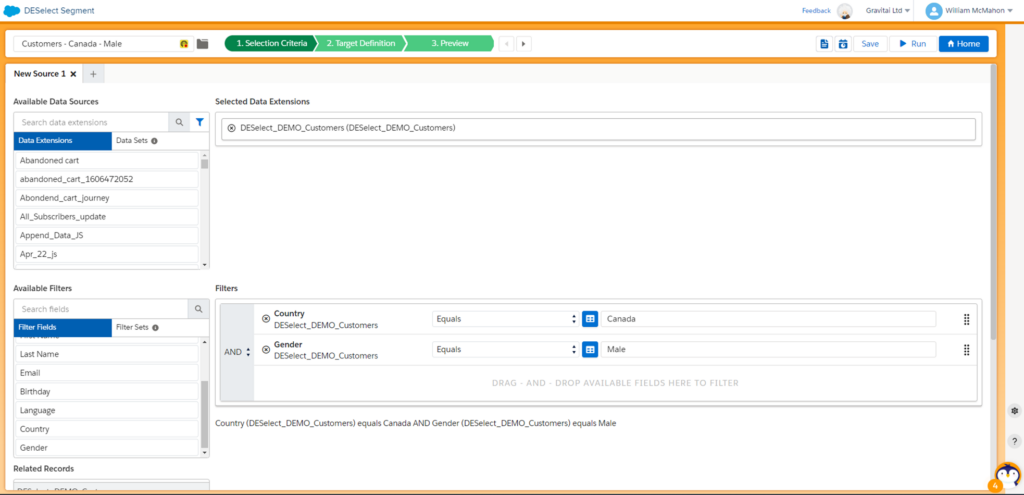
Circling back to the benefits of Query Studio, DESelect has similar functions.
Query Studio Benefit: Interactive Querying
DESelect Segment’s drag-and-drop interface is designed for marketers, allowing them to visually build complex queries without the need for extensive SQL knowledge. There’s SQL under the hood driving each query, but this intuitive approach makes it easier for marketers to engage with data and create targeted segments.
Benefit: Data Preview
Review data before submitting a query, previewing elements such as how many records your query will return, a detailed view of the created data extension, and any errors that would hinder results.
Benefit: Data Export
DESelect seamlessly integrates with Salesforce Marketing Cloud, ensuring smooth data flow between the platforms. This integration streamlines workflows and enhances productivity for marketers.
Benefit: Validation Tests
DESelect optimizes queries in the background, ensuring they run efficiently. This reduces the risk of query timeouts and allows marketers to focus on deriving insights from their data rather than troubleshooting performance issues.
Benefit: Reusable Templates
DESelect admins use segmentation templates for commonly run campaigns, in effect saving users’ time and preventing mistakes. Once you have templates in place, you can reuse them for similar segments in the future.
Here are some key ways that DESelect Segment improves on Query Studio:
Advantage: The Scope of Advanced Segmentation
DESelect Segment offers powerful segmentation features that are both user-friendly and robust. Marketers can create intricate data segments for various purposes, such as targeted campaigns, A/B testing, and audience analysis, leading to more personalized and effective marketing efforts.
Advantage: Guided Workflows
DESelect provides guided workflows that walk users through the data querying and manipulation process step by step. This guidance reduces errors and enhances efficiency, making it suitable for users of all skill levels.
Overall, DESelect empowers marketers to make the most of their data within Salesforce Marketing Cloud, whether they are SQL experts looking for optimized performance or newcomers seeking a more user-friendly interface. It’s a valuable tool for data-driven marketing that makes complex tasks more accessible and efficient.
How to Get Started with DESelect
Beginning your journey with DESelect is a straightforward plug-and-play process designed to quickly get you started harnessing the power of your data within Salesforce Marketing Cloud.
DESelect works with a list of certified implementation partners, to provide teams new to Marketing Cloud with top-tier solutions and expertise within the Salesforce ecosystem.
Learn how to find the best solution for your segmentation needs.

William McMahon
CEO & Founder at Gravitai, William has over 15 years experience in the CRM world as both a top UK Salesforce Partner and Ex-ExactTarget Principal Solutions Architect.

