Salesforce Marketing Cloud, one of the most powerful marketing automation tools available today, offers robust functionalities for marketers to manage customer journey touchpoints. A key element of this platform is the ability to segment customers, allowing for highly personalized experiences.
This blog post will explain the fundamental concepts you need to understand about how to segment in Salesforce Marketing Cloud, specifically data extensions, segmentation, personalization, and deduplication.
Understanding Data Extensions
In Salesforce Marketing Cloud, data extensions are essentially your means of storing data. These can be thought of as tables of data, similar to a Google or Excel spreadsheet. A data extension includes several fields, often referred to as metadata. This metadata provides an overview of the type of data stored in the data extension. For instance, a data extension might have fields such as first name, last name, email address, and phone number, all of which will help categorize your contacts.
One key field that every data extension should have is an ID field. An ID is essentially a string of characters that helps identify a contact. Having a unique identifier for each contact ensures that even if you have two contacts with the same first name or the same email address, you can still distinguish between them and send them personalized marketing communications.
The Essence of Segmentation
So, in what context can you segment in Salesforce Marketing Cloud? Essentially, creating a segment is about creating a list of records with specific attributes or characteristics. This list is usually created based on certain filters applied to your data extension.
For instance, if you want to create a segment of contacts that live in a particular city, you would apply a filter to your data extension based on the city field. This essentially narrows down the data records to include only those contacts that live in the specified city. Segmentation is a powerful tool for personalizing your marketing campaigns, as it allows you to target specific groups of contacts based on their attributes.
Demystifying Deduplication
In the world of data management, it is common to encounter duplicates in your database. This can occur due to various reasons such as multiple form submissions by the same person or accidental data entry errors. Duplicate records are undesirable for several reasons, one being that they can inflate your Salesforce bill, as Salesforce charges based on the number of contacts in your database.
Deduplication involves identifying and removing these duplicates. To later effectively segment in Salesforce Marketing Cloud, deduplication is done using filters, SQL, or DESelect functions. The aim is to ensure that each contact in your database is unique, thereby improving the accuracy of your data and the effectiveness of your marketing campaigns.
Joining Data Extensions
If you’ve wondered about combining or enriching data extensions, you’re talking about joining. This process, most commonly referred to as a “join,” is a SQL command used for querying a database. Essentially, it’s a way of merging different sets of data for a comprehensive view.
But to make this happen, you need more than one data extension. For instance, consider a Mexican food delivery app that has two tables: “Customers” and “Orders.” The “Orders” table records every purchase, each given a unique ID, item description, and price.
However, to understand who’s buying what, we must associate these orders with specific customers. This is where joins come into play. Each order’s record includes the customer ID, linking it back to the “Customers” table. So if we want a comprehensive list of customers and their respective orders, we create a new table – a join of the “Customers” and “Orders” tables. This operation enriches our data and allows for better data analysis.
Segmenting Joined Data
Once the data is joined, segmentation becomes an important process. Often, we want to segment data based not only on demographic information but also customer behavior. For instance, we might be interested in those who order burritos frequently.
This is where a joined Data Extension comes in handy. It allows us to filter the data, letting us find everyone who ordered burritos, for example. In essence, the join operation enables more targeted and efficient segmentation by combining relevant data.
Deduplicating Joined Data
Data deduplication is a critical aspect of managing joined data. Since the process of joining can create multiple records for a single customer, removing these duplicates helps maintain a clean, accurate data set.
Typically, we might want to send just a single email to a customer, even if they’ve made multiple orders. Therefore, deduplication ensures that customers receive only unique, relevant communications. In our Mexican food app, for instance, deduplication would be based on the email column, ensuring each customer, regardless of their number of orders, appears just once.
The essence of joining, segmenting, and deduplicating data is about enabling us to understand and serve our customers better. With these processes, we can combine, analyze, and make use of our data effectively.
The Relationship Between Personalization and Segmentation in Salesforce Marketing Cloud
Finally, we’re bringing everything full circle. We’ve segmented lists, joined them, and deduplicated these joint lists to enhance our communications with customers. This process of segmentation in Salesforce Marketing Cloud helps us narrow down the right people we want to contact, but it also sets the stage for personalization.
Using the customer’s first name is the most basic form of personalization. However, when we enrich our data by joining different data extensions, like ‘Customers’ with ‘Orders’, our emails become more personalized and relevant. For instance, we can acknowledge specific purchases, saying, “Thank you for buying your [item] for [price].”
Conclusion
The essence of these data management strategies is to foster a more engaging and meaningful connection with your customers. By ensuring your data is accurate, targeted, and personalized, you communicate more effectively and provide a better experience. These techniques ultimately allow your data to work for both you and your customers.

More than 70% of nations have enacted data protection and privacy laws in the last decade, as shown by the 241 legislations listed on the United Nations Trade and Industry website. The pressing question arises: How do multinational teams navigate the complexities of data privacy compliance, especially when adopting Salesforce Marketing Cloud (SFMC), as it ingests their customers’ data to generate insights and facilitate communication across diverse channels?
Those versed in CRM administration, as well as creative and technical marketing, often attest to undergoing data privacy training preemptively, aligning with regional legislation. Such training is especially important for individuals with system access privileges and those handling the data directly. According to Salesforce’s website, the company diligently monitors the evolving global privacy landscape, adjusting its privacy program to remain abreast of changes. |
This article delves into the influential data privacy legislative and regulatory frameworks impacting multinational teams, the challenges multinational organizations encounter, and how streamlining collaboration can lead to better compliance. It further sheds light on compliance best practices that can be executed using SFMC, encompassing useful system and automation functionality that culminate in effective and efficient communication with subscribers. |
Legal and Regulatory Frameworks Impacting Multinational Teams |
Diverse regulations worldwide emphasize distinct facets of data privacy, focusing on specific rules within each jurisdiction. The landscape of data privacy laws is continually evolving, affecting multinational teams as they navigate compliance across these jurisdictions. This dynamic environment traces back to the initiation of the EU’s General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in 2018, serving as a catalyst for the establishment of region-specific data protection laws globally. The GDPR’s foundational principles are:
These principles left their mark on the various laws that followed, prompting multinational teams to devise compliance strategies that align emerging laws with the principles of the GDPR. As illustrative instances, consider subsequent jurisdictional laws such as the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA), the Personal Information Protection and Electronic Documents Act (PIPEDA), and the General Data Protection Law (LGPD). The CCPA mandates businesses disclose data sharing practices, providing residents with rights to access, delete, correct, and opt-out of data sharing. PIPEDA, applicable in Canada, safeguards personal information in the private sector, governing its collection, use, and disclosure for commercial activities. LGPD in Brazil safeguards the privacy of personal data collected or processed within the country. Consider a scenario where all the previously mentioned laws apply to a multinational team. To navigate this intricate framework effectively, the team must initially grasp the fundamental principles of the GDPR as a robust foundation. To expand on this, they need to familiarize themselves with the specific data privacy laws governing their operational regions and sectors. A deep understanding of personal data regulations in both their home jurisdiction and others is imperative. Crucially, the team’s digital marketing solutions must align with legislative requirements. By identifying commonalities and nesting pertinent laws, multinational teams can ensure comprehensive compliance. This not only involves adhering to the similar requirements they find, but also addressing diverse and stringent regulations that are specific to jurisdictions, thereby mitigating the risk of costly penalties. |
Challenges and Considerations of Data Privacy Compliance in Multinational Teams |
Multinational teams contend with significant external and internal pressures concerning data compliance, impacting various business drivers such as cost, personnel, processes, technology, quality, and risk scope. Externally, escalating pressure results from the emergence of diverse global legal requirements, which have been characterized as impeding progress in life and business advancements in certain analyses. Internally, organizations must navigate this evolving regulatory landscape, ensuring that their data compliance policies align with changing regulations. Consequently, internal dynamics necessitate continuous updates to data governance structures, intensifying the impact on organizational policies and processes. This confluence of external and internal forces presents growing challenges for multinational teams in adhering to data compliance, resulting in a surge in associated costs. Common initiatives that contribute to this cost escalation include the following.
External forces, such as the rising demand for personalization from customers, add another layer of complexity. To stay competitive, organizations must invest in processes, personnel, and technology to meet evolving customer expectations. This requires navigating the delicate balance between adhering to data regulations that vary across regions and meeting dynamic customer demands. Internally, aligning data privacy compliance policies with multinational contexts introduces further complexity. More resources are spent on tailoring training programs for diverse cultural contexts and to overcome language barriers. This has become essential to address jurisdictional requirements that speak to lawfulness, fairness, and transparency. The industry shift to cloud solutions exposes data to cybersecurity risks, necessitating a steadfast commitment to data integrity and confidentiality. Multinational teams must implement robust data security measures to comply with diverse breach notification requirements. Given the variation in these requirements across jurisdictions, teams must prepare to adhere to different reporting timelines and specifications in the event of a data breach. Moreover, establishing a compliance team in multinational settings poses its own set of challenges. This endeavor is not only costly, but also requires increased accountability, leadership support, alignment with the business’ key performance indicators (KPIs) and establishing appropriate reporting structures. This is further discussed in the below section. |
Streamlining Communication and Collaboration Across Business Units |
The establishment of an effective team for data compliance necessitates not only the identification of suitable personnel but also the assurance that these individuals assume accountability and responsibility for the pertinent compliance processes and data. The imperative here lies in maintaining an open communication loop addressing concerns related to data compliance, accuracy, and accountability. In instances where accountability ownership cannot be discerned, a prudent course of action would be to eliminate the associated data and its interconnected elements. There are various Data Governance Framework suggestions, but in the case of a multinational organization a Centralized Enterprise Data Quality and Governance Team, in collaboration with dispersed teams, is often most effective. The team may comprise of Data Governance Councils and appointed Data Stewards who oversee critical data domains. This includes, for example, designating a Data Steward for Marketing Operations and another for Customer Success and so forth. The role of these stewards is to enforce compliance rules, monitor data quality, and ensure overall data integrity. In the context of multinational operations, it is sensible to designate regional Data Stewards or Business Unit Data Stewards reporting to the Centralized Enterprise Data Quality and Governance Team. Their mandate would involve overseeing processes, ensuring accountability, monitoring data quality, and upholding security rules. This structure will empower individual business units to articulate the purpose of their data, take responsibility for its accuracy, manage access permissions, and ensure data consistency. The Centralized Data Quality and Governance Team assumes a pivotal role not merely in appearance but in substance, requiring the formalization of programs designed to address financial losses, mitigate data privacy compliance risks, and navigate the continual evolution of data compliance standards. These programs may be extended to regional implementation where required and administered through collaboration with the designated Data Stewards. These programs are crucial for organization-wide compliance and to secure the support and engagement of organizational leadership, especially when Data KPIs align with overarching Business KPIs. Alignment will elevate the significance of data governance beyond mere regulatory adherence to a strategic imperative integral to the organization’s mission. |
Best Practices for Ensuring Data Compliance in Salesforce Marketing Cloud |
As highlighted earlier, the impact of data compliance on revenue and costs requires thorough internal data governance practices and policies. It is imperative to also ensure alignment across your SFMC instance. Here are some recommended best practices within SFMC, which is not an exhaustive list. Business Unit PartitioningIn a multinational company, distinct business units may operate under the same enterprise account in SFMC. Your governance framework may dictate that these units should not access each other’s data. Configure this in SFMC by navigating to Setup/Business Units. For data sharing between business units, consider using shared data extensions and establish permissions using SFMC Data-Extension policies. Field-Level EncryptionTo enhance compliance with data privacy policies or regulatory requirements, activate field-level encryption, particularly for email addresses in SFMC. This added protection sets selective encryption for desired fields of a data extension before it is sent to Marketing Cloud. This ensures sensitive data remains private from Salesforce and any team members without proper clearance. Administrator Roles and PermissionsAlign your SFMC Administrator Role with your Data Governance Framework on access controls and permissions. Utilize SFMC standard roles like Marketing Cloud Administrator, Marketing Cloud Viewer, etc., or customize roles to fit your organizational structure. Send Classification SetupLeverage your governance framework to guide the setup of Send Classifications (promotional/commercial or transactional emails) in SFMC. This includes configuring sender profiles (email addresses used for sending) and delivery profiles (standardized headers and footers) to ensure compliance with regulations such as CAN-SPAM. Content Management and TaggingImplement tagging in SFMC to manage and identify content subject to specific regulations and policies. This facilitates easy tracking, identification, and management of created content, thereby customer communications remain compliant. Data Retention PoliciesRefer to your Data Governance Framework to determine the duration for which data should be retained. Configure and edit data retention policies within SFMC Data Extensions accordingly. Contact Data Deletion ProcessUtilize the available manual process in SFMC for deleting all related data to a contact. This can be done through the Contact Builder in the All Contacts tab and all data will be deleted related to this contact. Consider automating this process, through development, to streamline data removal. Regular Compliance Audits and TrainingConduct regular data privacy compliance audits and assessments. Ensure that all staff with data access undergo training to be well-versed in the organization’s data governance policies and relevant jurisdictional requirements. This proactive approach minimizes the risk of non-compliance. By adhering to best practices and continuously assessing and educating your staff, your organization can effectively navigate the complexities of data compliance within SFMC, thereby mitigating potential financial impacts. |
Data Compliance Automation in Salesforce Marketing Cloud |
Aligned with data privacy and compliance best practices, SFMC offers automated functions to facilitate adherence to compliance standards. SFMC recommends the deployment of monitoring tools, such as Google Postmaster Tools and SNDS with Microsoft, to oversee IP and Domain reputation, detecting potential issues like compromised servers, malware, viruses, and botnets. SFMC also equips users with tools and functionalities which, if implemented diligently and according to jurisdictional rules, can ensure compliance. Here are some automation features that can be set up within SFMC: Automate Subscriber Consent Management
Automate Contact DeletionAddress right-to-be-forgotten regulations by automating contact data deletion in SFMC. This may involve further development efforts to ensure data privacy compliance. Alternatively, contacts can be added to do-not-send contact lists, acting as an auto-suppression list to prevent further sends to unsubscribed or problematic contacts. Automated Restrictions on Data ProcessingLeverage the Marketing Cloud REST API to automate restrictions on data processing for specific contacts. This helps marketers adhere to subscribers’ privacy preferences when managing their data. Unsubscribing Nonactive RecipientsAlthough SFMC doesn’t automatically unsubscribe nonactive recipients, it does recognize bounced emails, preventing further communication in the case of hard bounces (user unknown or domain errors). Automate Audience SegmentationUse filter activities and queries in SFMC to automate the segmentation of audiences. This ensures that campaigns are directed to targeted audiences based on their preferences and consent, enhancing relevance. Automate segmentation of audiences for relevant content sends in SFMC with filter activities and queries. This will create targeted audiences for campaigns and ensure that your marketing messages are directed only to individuals who will find the information relevant and have given their consent. Speaking of automating segmentation, DESelect removes the need for code when creating audiences, empowering all marketers to create the audiences they need. Learn how even brands in highly regulated industries, like financial services company Alm. Brand, have cut the time it takes to segment in half while remaining in compliance with privacy regulations. SFMC can integrate with other compliance tools and services. This can include tools for data anonymization, data masking, and other solutions that help in maintaining compliance with regulations. |
Conclusion |
In summary, effectively maneuvering through the intricate landscape of data privacy compliance across multinational teams, utilizing SFMC, demands a meticulous and committed approach. This involves assigning explicit roles and responsibilities for continuous accountability and responsibility. With over 70% of nations implementing data protection laws in the past decade, addressing compliance intricacies is paramount, affecting organizational data governance policies and procedures. |

Suzaan Groves
Suzaan is a Project Director at Cloud-Vision, where she specializes in managing projects related to Salesforce Marketing Cloud implementations and development. She has been part of project implementations in various sectors including automotive, retail, government and financial services. Suzaan is a certified Project Management Professional (PMP), and she holds an MBA from the University of Stellenbosch.

Structured Query Language (SQL) is a powerful programming language designed for managing data within relational databases. Similar to Excel, these databases organize information in tables, utilizing rows and columns to represent distinct data attributes and their relationships. SQL enables users to execute commands for storing, updating, removing, searching, and retrieving data, contributing to efficient database management.
Widely embraced across diverse applications, SQL is favored by data analysts and developers for its seamless integration with various programming languages, such as Java. Its user friendly nature, employing common English keywords, makes SQL accessible for learners and facilitates the creation of high-performance data processing applications.
For those who want to learn how to write SQL, we will review concepts specific to Marketing Cloud, the parts of a query, and applying these queries to common use cases.
RELATED: Script Activity – The underrated SFMC powerhouse
What is SQL used for in Salesforce Marketing Cloud?
In Salesforce Marketing Cloud, data extensions act like tables for storing and organizing data. They help structure information within the platform, allowing users to interact with and manipulate data in these extensions, in turn facilitating smooth integration into marketing efforts and analytics.
These extensions can store diverse data like customer details, preferences, and buyer behavior. SQL queries offer a robust way for marketers to efficiently extract, filter, and organize data within these extensions.
SQL Essential Tasks
Querying and Manipulating Data
Querying with SQL empowers marketers and administrators to pinpoint precise data among complex datasets and manipulate it, enabling users to transform and organize information to align with marketing goals. This capability not only streamlines analysis and operations but also ensures extracted data is structured effectively for activation. Ultimately, SQL in Salesforce Marketing Cloud goes beyond surface-level activity, unlocking a more powerful understanding of the customer base for data-driven marketing strategies.
Extracting and Filtering Data
SQL queries serve as a strategic tool, allowing users to sift through large volumes of information and focus solely on relevant data, simplifying the complex process of data extraction. The versatility of SQL is evident in its filtering capabilities, enabling marketers to pinpoint specific criteria crucial to their objectives.
Whether isolating data based on demographics, customer preferences, or behavioral patterns, SQL’s filtering functionality offers precise control that not only streamlines data extraction but also ensures the relevance of extracted information.
By leveraging SQL for data extraction and filtering in Salesforce Marketing Cloud, users optimize workflows, removing the need to manually hunt through data extensions. This targeted approach not only saves time but also ensures the extracted data is complete and accurate.
Organizing Data
SQL efficiently organizes data, offering robust tools beyond data retrieval. It establishes a coherent structure within databases, aligning with the analytical and reporting needs of marketers and administrators. This structured format ensures data is stored for effective analysis, fundamental for extracting meaningful insights and informed decision-making.
SQL enables the creation of easily navigable databases optimized for marketing strategies, laying the foundation for streamlined reporting. This organized data architecture enhances overall efficiency in data management, empowering users to make confident, data-driven decisions within Salesforce Marketing Cloud.
Segmentation of Audiences in Marketing Campaigns
In Salesforce Marketing Cloud, knowing how to write SQL queries plays is pivotal to marketers aiming to finely segment their customer base. SQL facilitates the strategic division of customers into distinct groups based on factors like demographics, preferences, and previous interactions.
SQL’s instrumental role in audience segmentation lies in its ability to analyze and interpret diverse datasets. Marketers craft SQL queries to pinpoint specific criteria, allowing for the creation of targeted segments that move beyond broad categorizations, offering a nuanced understanding of the customer base.
Segmentation criteria can vary widely, from geographic location to purchase history or engagement levels. With SQL’s capabilities, marketers gain the flexibility to define these criteria precisely, ensuring each segment is tailored to unique characteristics and behaviors.
Once audiences are segmented, marketers can deploy highly targeted and relevant marketing messages to each group. This level of personalization enhances campaign effectiveness, as messages resonate more directly with the specific interests and needs of each segment. Ultimately, SQL’s role in audience segmentation within Salesforce Marketing Cloud becomes a cornerstone for delivering impactful and tailored marketing experiences to diverse customer groups.
Facilitating Personalized Communication
SQL emerges as a powerful tool for marketers aiming to enhance their communication strategies. Through strategic use of SQL, marketers craft campaigns that go beyond generic messaging, focusing on targeted and personalized communication through specific audience criteria.
SQL’s ability to interact with customer attributes tailors campaigns to individual preferences. Marketers often use SQL queries to identify specific customer segments based on demographics, purchase history, or engagement patterns, allowing for the creation of campaigns that speak directly to the unique characteristics and interests of each segment. This personalized communication resonates more deeply with these audiences, establishing a meaningful connection more likely to drive conversions and purchases.
In essence, SQL’s role in Salesforce Marketing Cloud goes beyond data manipulation – it becomes a catalyst for elevating communication strategies, where each message is not just targeted but genuinely resonant with the diverse needs of the audience.
How to Write SQL: The Parts of a Query
In a SQL query used for Salesforce Marketing Cloud, several key components come together to retrieve, manipulate, or manage data. Here’s an overview of the essential parts:
SELECT Clause
Specifies the columns or fields to be retrieved from the database. For example, SELECT FirstName, LastName would retrieve data from these specific columns.
FROM Clause
Specifies the source table or data extension from which the data is being retrieved. For instance, FROM Contacts indicates that the data is sourced from the “Contacts” table or data extension.
WHERE Clause
Conditions that filter the rows of data returned by the query. It allows you to specify criteria, such as WHERE Age > 25, to retrieve only records where the age is greater than 25.
ORDER BY Clause
Determines the order in which the results are presented. For instance, ORDER BY CreatedDate DESC would arrange the results based on the “CreatedDate” column in descending order.
GROUP BY Clause
Groups rows that have the same values into summary rows, typically used with aggregate functions like COUNT, SUM, AVG. For example, GROUP BY Country groups data by the “Country” column.
HAVING Clause
Works in conjunction with GROUP BY and allows filtering on grouped results. It’s conditional, similar to the WHERE clause, but applied after the grouping has occurred. For example, when grouping by country, HAVING COUNT(CustomerID) > 5 will only include results where there are more than five results for a given country.
JOIN Clause
Specifies how tables or data extensions are related to each other. For instance, INNER JOIN Orders ON Customers.CustomerID = Orders.CustomerID would join the “Customers” and “Orders” tables based on the “CustomerID” column.
LIMIT/OFFSET Clause
Controls the number of rows returned and can be useful for paginating results. For example, LIMIT 10 OFFSET 20 would retrieve 10 rows, starting from the 21st row (offsetting the first 20).
Now you know how to write SQL. These components collectively form a query, allowing users to interact with and retrieve specific subsets of data from Salesforce Marketing Cloud databases or data extensions.
Essential SQL queries used in SFMC
Selecting Data
To retrieve specific columns from a Data Extension:
```sql
sql
SELECT FirstName, LastName, Email
FROM ContactDataExtension
```
Filtering Data
To filter data based on a specific condition:
```sql
sql
FROM PurchaseDataExtension
WHERE PurchaseAmount > 100
```
Joining Data
To combine data from two Data Extensions based on a common field:
```sql
sql
SELECT Orders.OrderID, Customers.CustomerName, Orders.OrderDate
FROM Orders
INNER JOIN Customers ON Orders.CustomerID = Customers.CustomerID
```
Grouping and Aggregating Data
To group data and calculate aggregates (e.g., total purchases per customer):
```sql
vbnet
SELECT CustomerID, COUNT(OrderID) AS TotalOrders, SUM(OrderAmount) AS TotalAmount
FROM OrderDataExtension
GROUP BY CustomerID
```
Ordering Data
To sort data in ascending or descending order:
```sql
sql
SELECT ProductName, Price
FROM ProductDataExtension
ORDER BY Price DESC
```
Limiting Results
To retrieve a specific number of rows:
```sql
sql
SELECT
FROM SubscriberDataExtension
LIMIT 10
```
Combining Filters
To apply multiple conditions using AND or OR:
```sql
sql
SELECT
FROM CustomerDataExtension
WHERE Age > 25 AND Country = 'USA'
```
SQL is essential for creating the right audience, but how do you personalize content to ensure you create the right message? Learn the basic overview of AMPscript.

In today’s digital landscape, where customer experiences reign supreme, the strategic use of data has become a pivotal factor in achieving success in each marketing campaign launch. Your ability to harness and leverage data effectively often means the difference between a captivating customer journey and one that falls short of expectations.
To navigate this data-driven world with finesse, one tool stands out as a beacon of opportunity: Salesforce Journey Builder.
We’ll embark on a comprehensive exploration of how to prepare your data for seamless integration with Journey Builder.
This isn’t solely about automation; it’s all about creating personalized and meaningful experiences for your audiences. Come along with us as we explore the details of data storage, taxonomy, and deployment, making sure your data is prepared to power the vibrant customer journeys you’ve envisioned.
The path to success begins here, as we decode the secrets to maximizing the potential of Journey Builder through smart data practices.
Buckle up, and let’s prepare your data for a journey of a lifetime.
The Foundation: Optimal Data Storage
Benefits of Best Practice Data Storage
A top-notch data storage strategy has numerous advantages if carefully planned and implemented. For example:
- More secure data: This is because measures are taken to mitigate threats and provide ongoing visibility into data access patterns and potential risks.
- Compliance: Ensure data and storage management complies with applicable regulations and can meet auditing requirements.
- Continuous use: Systems, processes and data protections are put into place to ensure ongoing availability and reliability, resulting in greater user productivity and customer satisfaction.
- Long term use: Storage devices provide the capacity necessary to meet current and future workloads, while accommodating different types of data, without over-provisioning storage hardware.
- Adaptable operations: Storage systems are flexible enough to scale as demand fluctuates, while reacting to changing requirements and accommodating new storage technology.
- Comprehensive: Storage systems are easier to manage and monitor, and deploying storage devices is faster, often without the compatibility and integration issues that come with siloed or piecemealed storage systems.
Data Storage Options For Marketing Cloud Teams Within SFMC
In the world of Salesforce Marketing Cloud, the choice between Lists and Data Extensions is a pivotal decision, one that can significantly impact the efficiency and effectiveness of each marketing campaign launch. Both options come with their unique advantages and disadvantages, making it essential to evaluate which aligns best with your campaign needs.
What Are Salesforce Marketing Cloud Lists?
In Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s Email Studio, lists serve as a foundational approach for managing subscriber data. Essentially, a list in this context is akin to a digital roster, compiling a group of subscribers. This setup facilitates the task of dividing your audience into distinct segments for targeted communication.
When you add subscribers to a list, you have the capability to assign various attributes to them. These attributes act like labels or markers, offering insights into each subscriber’s current engagement or status in relation to that specific list. For instance, you might track whether a subscriber is active, inactive, or has opted out of communications.
However, it’s important to note that the use of lists is more suitable for scenarios where the total number of subscribers doesn’t exceed 500,000. This limitation is crucial to keep in mind for scalability and efficiency reasons. Lists are particularly effective for straightforward subscriber models, where the primary focus is on basic subscriber management without the need to delve into more complex data like transactional history or detailed commercial interactions.
Moreover, lists in Salesforce Marketing Cloud are also adept at handling personal subscriber data. This means you can manage information such as email addresses, names, or other personal details within these lists, ensuring that your communications are personalized and relevant.
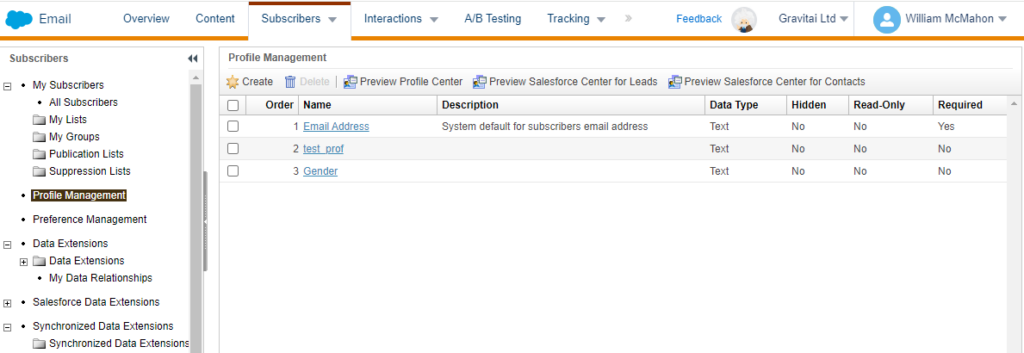
Image: Lists use ‘Profile Attributes’ which are applied consistently across all Lists in SFMCAdvantages of Lists:
Simplicity: Lists are straightforward to create and use, making them an excellent choice for simple email sends. With Lists, you can quickly import email addresses and start sending campaigns without intricate setup.
Basic Segmentation: Lists enable basic segmentation based on attributes like email addresses, suitable for simpler campaigns.
Disadvantages of Lists:
Data Duplications: Duplicate email addresses across different Lists can lead to data inconsistencies and maintenance challenges.
Limited personalization: Profile Attributes in SFMC are essentially standard fields that store subscriber information. When using Lists, these attributes are applied universally across all lists. This means that every list you create will share the same set of Profile Attributes, such as name, email address, and other basic subscriber details. Lists may not offer the level of personalization and dynamic content that Data Extensions provide.
Scalability: Lists are suitable to Subscriber counts below 500k records and for a simple (flattened) data model.
Usability in Journey Builder: Journey Builder does not support the use of lists as a data entry source.
What are Data Extensions?
In the realm of Salesforce Marketing Cloud, Data Extensions offer a versatile and robust way to manage and manipulate subscriber data, going beyond the basic capabilities of lists. Think of Data Extensions as sophisticated, customisable tables capable of storing vast and varied types of data, akin to spreadsheets but with enhanced functionality and integration capabilities.
Unlike lists, Data Extensions allow for a more intricate and detailed structuring of subscriber information. You can create multiple columns in a Data Extension, each designed to hold specific types of data, such as text, numbers, dates, or even Boolean values. This flexibility enables a deeper and more nuanced understanding of your subscribers, allowing for highly targeted and personalized marketing campaigns.
One of the key strengths of Data Extensions is their scalability. They comfortably handle large volumes of data, making them ideal for organizations with extensive subscriber bases or those dealing with complex data sets, including transactional details, behavioral data, and more.
Moreover, Data Extensions are not just siloed data repositories. They are designed to seamlessly integrate with other parts of the Salesforce Marketing Cloud ecosystem, such as Journey Builder and Automation Studio. This integration means that the data within Data Extensions can trigger specific actions, feed into automated marketing workflows, and inform real-time interactions with subscribers.
Furthermore, Data Extensions provide advanced segmentation capabilities. You can use SQL queries to segment and manipulate data, offering a level of precision in targeting that goes beyond basic lists. This feature is particularly valuable for creating highly customized marketing campaigns or for performing in-depth data analysis.
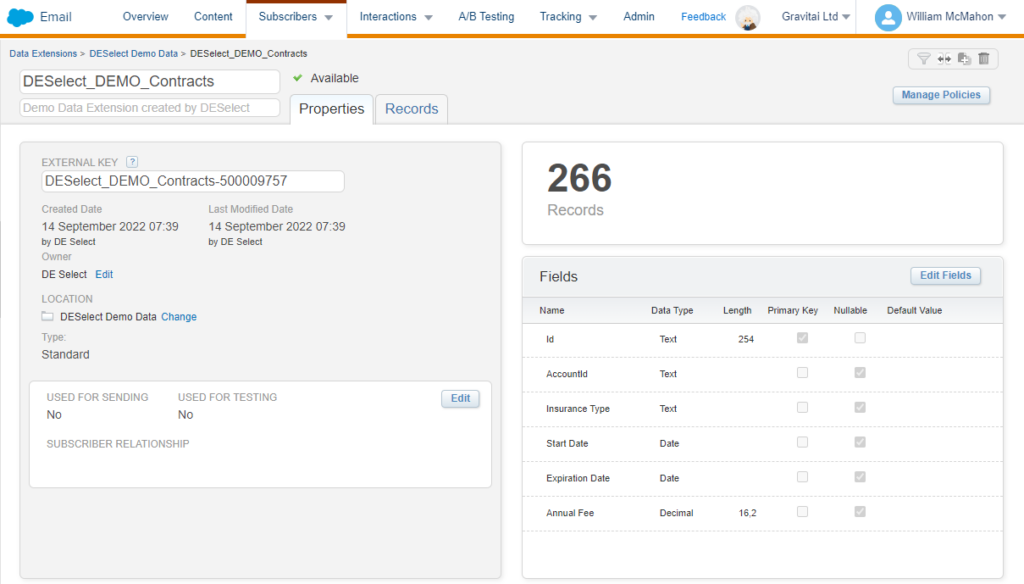
Image: Data Extensions allow you to create Fields/Attributes specific to each Data ExtensionAdvantages of Data Extensions:
Flexibility: Data Extensions are highly adaptable and can store a wide range of data fields, making them suitable for comprehensive customer data storage.
Robust Segmentation: Data Extensions offer advanced segmentation capabilities, allowing targeted campaigns based on multiple attributes.
Personalization: Data Extensions empower you to create highly personalized and dynamic content, catering to individual subscriber attributes.
Disadvantages of Data Extensions:
Complexity: Data Extensions can be more intricate to set up and manage, especially for handling large volumes of data and complex relationships.
Data Hygiene: Greater flexibility necessitates diligent data hygiene efforts to maintain data quality.
In summary, Lists are ideal for simpler campaigns with basic segmentation and uncomplicated list management. On the other hand, Data Extensions offer more flexibility, segmentation capabilities, and personalization options.
However, they require a deeper understanding of Salesforce Marketing Cloud and additional attention to data hygiene.
Ultimately, your choice should align with your specific marketing campaign launch needs and your team’s familiarity with Salesforce Marketing Cloud. For complex, personalized campaigns, Data Extensions are often the preferred choice, offering the versatility and capabilities needed to drive marketing success.
External Data Storage: How To Connect to SFMC
Integrating Salesforce Marketing Cloud with external data storage solutions presents both opportunities and challenges. The choice between local Marketing Cloud storage and external storage hinges on data volume, complexity, and specific use cases. Let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of both approaches:
Integrating with External Data Storage
While many businesses use an external database or CRM as their primary source of customer information, integrating these systems with Salesforce Marketing Cloud (SFMC) is essential for effective email marketing. In practice, businesses often synchronize key customer data from their master database into SFMC.
This approach allows for maintaining detailed and specific records externally while leveraging SFMC’s robust email marketing capabilities. The synchronization process involves importing essential information into SFMC that is crucial for segmenting and personalizing email campaigns. For more nuanced and detailed data, SFMC can access the external database via API calls. This method retrieves additional insights and information as needed to further tailor and enhance email communication.
Employing this integrated approach ensures that email campaigns are both personalized and relevant, drawing on a comprehensive understanding of customer profiles from both the SFMC and the external database systems. This strategy strikes a balance between the richness of data from the external databases and the specialized marketing tools available in SFMC.
Pros:
Data Consolidation: External storage centralizes customer data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive view of your customers by consolidating data from Salesforce, external CRMs, and third-party systems.
Data Enrichment: External storage enriches customer data with additional information, such as demographics or behavioral data, augmenting your understanding of customers.
Advanced Analytics: Data stored externally can be more accessible and amenable to advanced analytics tools, offering deeper insights for personalized marketing campaigns.
Real-time Data Sync: Many external data storage solutions offer real-time data synchronization, ensuring you have the latest customer information available for your campaigns.
Cons:
Complex Integration: Integrating external data storage with Salesforce Marketing Cloud can be intricate and may require custom development, APIs, or middleware solutions.
Data Security: Maintaining data security and compliance across external storage can be more challenging and may necessitate additional security measures.
Data Latency: Depending on the integration setup, accessing external data may introduce some latency, potentially affecting the real-time nature of your marketing campaigns.
Using Local Salesforce Marketing Cloud Storage
Using local Salesforce Marketing Cloud storage as an alternative to integrating with external databases involves importing larger quantities of data directly into SFMC.
This approach is particularly viable when businesses prefer to have immediate access to a substantial amount of data within their marketing platform for quick campaign launches. However, it’s crucial to import only data that is relevant to the marketing campaigns to maintain efficiency and relevance.
Mirroring the data architecture of the source system within SFMC is recommended to ensure consistency and ease of navigation. The data can be imported either through a Batch File Import Process or via API, depending on the volume and frequency of data updates required.
It’s important to note that in this model, SFMC serves as a “slave” to the source system, meaning it reflects the data from the primary database but does not override or become the master repository of data. This approach allows SFMC to utilize a comprehensive set of data for enhanced targeting and personalization in marketing campaigns while maintaining the integrity and primary control of data in the original source system.
Pros:
Simplified Setup: Local storage in Salesforce Marketing Cloud is straightforward and requires no external integrations. It’s an out-of-the-box solution.
Data Privacy: Local storage provides a higher level of data privacy and control. This is a critical factor for businesses that need to adhere to strict data security and compliance standards.
Out-of-the-Box Integration: Local storage seamlessly integrates with Salesforce Marketing Cloud’s native features, making it suitable for standard use cases.
Cons:
Storage Limits: Salesforce Marketing Cloud has storage limits that may be insufficient for organizations with large volumes of customer data.
Data Fragmentation: Using local storage may result in fragmented customer data, particularly if data is spread across different Salesforce instances.
Data Security and Compliance: The importance of maintaining data security and compliance with relevant regulations
Getting ready for a campaign launch is a meticulous undertaking, with each detail carefully planned to secure success. Amidst many strategic factors, it’s vital to keep a keen focus on data security and compliance.
In the contemporary landscape, ensuring data security and compliance with applicable regulations is not merely a recommended practice – it’s an absolute necessity.
Data Security: Protecting your data from unauthorized access and breaches is paramount. Whether it’s customer information, transaction records, or sensitive campaign data, robust data security measures are essential. Implementing encryption, access controls, and regular security audits are just a few strategies to fortify your data’s defenses.
Regulatory Compliance: When it comes to data protection regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or CCPA, it’s not just a matter of checking boxes – it reflects an organization-wide commitment to treating data with respect and responsibility. Failing to comply can result in significant consequences, from legal penalties to reputational harm. To maintain compliance, it’s crucial to stay updated on the latest regulations, put the necessary processes in place, and routinely conduct audits.
Customer Trust: Beyond legalities, data security and compliance play a crucial role in building and maintaining customer trust. When your customers know their data is handled with the utmost care and in line with legal standards, they’re more likely to engage with your campaigns and share their information with confidence.
In conclusion, data security and compliance are integral components of campaign readiness. They ensure that your data is not only prepared for campaign success but also protected from potential pitfalls. Prioritizing these aspects safeguards your reputation, strengthens customer trust, and enables your campaigns to thrive in an environment of data privacy and security.
Data Quality Assurance: Ensuring Data Integrity and Cleanliness
As marketers, we understand the power of data in crafting compelling and effective campaigns. It’s the lifeblood of our strategies, driving us toward our goals and objectives. However, data alone is not enough.
It’s the quality of data that truly makes the difference. That’s where Data Quality Assurance steps in, playing a strategic role in ensuring data integrity and cleanliness for a campaign launch that hits the mark.
Data Integrity: The first pillar of Data Quality Assurance is maintaining data integrity. This ensures that your data remains accurate, dependable, and consistent. Inconsistencies or errors within your data could potentially lead to costly mistakes and the dissemination of inaccurate information, ultimately undermining the effectiveness of your campaign.
Data Cleanliness: Data must be free from errors, duplicates, and inconsistencies. Ensuring data cleanliness is crucial to prevent costly mistakes in your campaigns, such as sending multiple emails to the same recipient or reaching out to the wrong audience.
Data Readiness: Data Quality Assurance involves making sure that your data is ready for marketing campaign launch. This means it’s well-structured, properly formatted, and available for immediate activation when you need it.
By giving prominence to Data Quality Assurance, you’re not just avoiding costly mistakes but also guaranteeing that your campaigns are founded on precise and trustworthy data. This, in effect, boosts the accuracy and effectiveness of your marketing endeavors, resulting in superior outcomes and a deeper connection with your audience.
Organizing Your Data: Taxonomy
Data taxonomy involves creating a hierarchy of categories and subcategories used to classify and organize data consistently and logically so datasets can be understood quickly.
The Benefits of Implementing Data Taxonomy
- Better Decision-Making: We’ve all been in a situation where the power of hindsight would have been helpful when deciding to create a more positive outcome. However, you can access a similar superpower to help in these situations simply by accessing the correct information in an efficient manner.
- Better Clarity and Communication: When the definitions of specific terms are clear, the data’s sources and meanings are clear. With these definitions and data organized, you can achieve more clarity and communication within your marketing operations.
- Better Data Quality: Building a data taxonomy within your business gives greater confidence in the quality of your data. Because there is a clear understanding of the structure of your data and a consistent naming convention and concise definitions, it helps to avoid errors and highlight if there are any inconsistencies in the data.
- Avoid Duplication: Another benefit of data taxonomy is the avoidance of duplication. A clear understanding of your data shows what datasets have been created so you can easily see if what you need already exists.
For example, if someone in marketing was looking for the lifetime value of a set of customers, they could check the database to see if this exists before requesting it.
Creating a Data Taxonomy Framework
Preparing your data for a successful marketing campaign launch is a pivotal step in ensuring that your marketing efforts hit the bullseye.
To achieve this, it’s crucial to establish a robust Data Taxonomy Framework. This framework encompasses three key elements: Categorization and Hierarchy, Naming Convention, and Metadata and Tagging.
- Categorization and Hierarchy: Start by categorizing your data into logical groups. Create a hierarchy that reflects the relationships between these categories. This structure aids in organizing data, making it easier to locate and work with, ultimately enhancing campaign precision.
- Naming Conventions: Consistency is key. Implement a standardized naming convention for your data elements. Having a well-established naming convention simplifies data comprehension and utilization for team members. It minimizes mistakes and guarantees that everyone is aligned and working together smoothly.
- Metadata and Tagging: Metadata provides context to your data. It describes its characteristics, origins, and usage. Coupled with tagging, metadata allows for quick and searchable data discovery. Properly tagged data simplifies the process of finding the right elements for your campaign.
By establishing a Data Taxonomy Framework that incorporates these elements, you create a solid foundation for your data.
This, in turn, guarantees that your campaign launch is not only seamless but also customized to engage the right audience with the right message. Be sure not to underestimate the significance of these fundamental data preparation steps – they can be the decisive factor in your marketing success.
Integration With Journey Builder
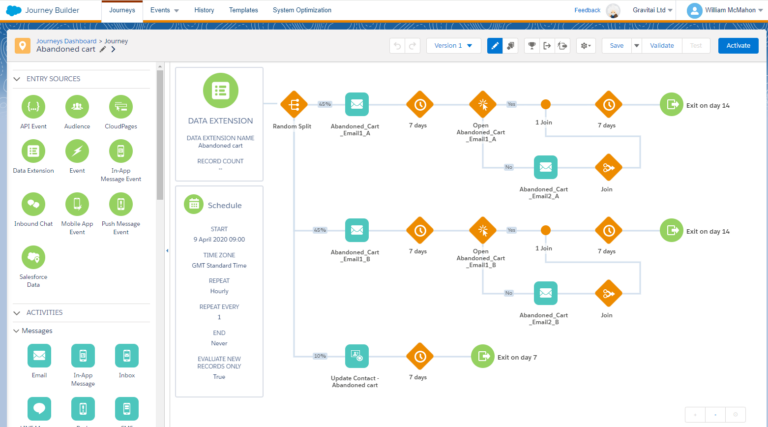
Salesforce Marketing Cloud Journey Builder is a dynamic and powerful tool designed to create personalized customer journeys. This studio allows marketers to craft tailored, multi-step interaction paths based on customer behavior, preferences, and data.
Think of a journey as a roadmap that guides each customer through a series of customized experiences and interactions with your brand. Journey Builder enables the orchestration of these experiences across various channels like email, mobile, social media, and more. It leverages real-time data and customer actions to adapt the journey dynamically.
In an example scenario, when a customer abandons a shopping cart, Journey Builder triggers a personalized email to bring them back. It’s not just about sending messages but about creating meaningful, timely, and relevant interactions that resonate with each customer. With its drag-and-drop interface, Journey Builder makes it easy to visualize and design these complex customer journeys, enhancing the overall customer experience and fostering deeper engagement.
Salesforce Journey Builder Integration is a multi-step process that requires careful planning and execution to maximize its potential. Let’s explore the key aspects of this studio.
Understanding The Significance of Journey Builder
Journey Builder goes beyond a mere marketing automation tool; it’s a strategic platform that empowers you to craft customer journeys that captivate and convert.
Delve into its core features and advantages to unlock the full potential of Journey Builder, making it a cornerstone of your marketing strategy.
Quick Journey Builder Intro
To begin, let’s dive into some of the key features and advantages of Journey Builder:
Multi-Channel Marketing: You’re empowered to interact with your customers through a diverse array of channels, spanning from email and SMS to the vibrant world of social media.
Segmentation: You can segment your audience for highly personalized messaging and offers.
Automation: Automation simplifies and streamlines your marketing efforts, saving time and resources.
Tracking and Reporting: Comprehensive analytics provide insights into your campaign’s performance.
Key Components of Journey Builder
Before diving into data preparation, let’s briefly review the fundamental components of Journey Builder:
Entry Sources: These are key repositories for where journey data comes from. They include Data Extensions, APIs, Cloud Pages and more. Note that you cannot start a journey using a List.
Activities: These represent the steps in a customer journey, such as emails, SMS messages, and wait times.
Triggers and Events: These initiate journeys based on customer actions or external events.
Decision Splits: These allow you to branch your journey based on actions, conditions or customer attributes.
Goals and Exits: These help to determine when a customer journey is considered successful and how it should end.
Data Preparation for Journey Builder Integration
Now that we have a basic understanding of Journey Builder, let’s focus on preparing your data for a successful integration. The effectiveness of your customer journeys heavily relies on the quality and structure of your data.
To make the most of your integration process, ensure data is thoroughly reviewed and cleaned to maintain data accuracy and consistency. This proactive step will ensure whatever data used for marketing campaign launch or impactful customer journeys will unlock the full potential of Journey Builder.
Here’s a detailed breakdown of the key steps to ensure your data is Journey Builder-ready.
Data Mapping: Aligning Stored Data with Journey Builder Requirements
Mapping your existing data to Journey Builder requirements is the first step in the data preparation process. It involves identifying and aligning the data fields in your current storage with the fields required by Journey Builder. This step ensures that your data seamlessly flows into the Journey Builder without any hiccups.
Key Considerations For Data Mapping
- Identify the essential customer data fields for your journeys
- Match your existing data fields with Journey Builder’s data extension fields
- Ensure data consistency and accuracy throughout the mapping process
Data Formatting and Transformation: Ensuring Data Is in the Right Format for Seamless Integration
Once you’ve mapped your data, the next step is to ensure it’s in the right format for integration. This involves cleaning and standardizing your data to ensure consistency. Inconsistent data can lead to issues during the integration process. Data formatting and transformation are crucial for a smooth Journey Builder experience.
Best Practices for Data Formatting
- Date Formats: Use a consistent date format (e.g., YYYY-MM-DD) to avoid confusion.
- Currency Symbols: Standardize currency symbols and ensure they are consistently applied.
- Duplicate Data: Remove duplicate entries to maintain data accuracy and reduce redundancy.
- Data Completeness: Verify that customer records are complete with all necessary information.
- Data Cleanliness: Cleanse data to remove any inconsistent or irrelevant information.
Testing and Validation: Strategies for Checking Data Integrity Before Deployment
Testing and validation are pivotal in the data preparation process. Before you launch your journeys, it’s essential to thoroughly test the data’s integrity. This includes checking for any missing or incorrect data, as well as verifying that the data flows correctly within Journey Builder. Comprehensive testing minimizes the risk of errors during deployment.
Data Validation Steps
- Conduct data integrity checks with data validation tools.
- Test your journey flows and interactions with sample data.
- Ensure that your data extensions are up to date.
Issues You Can Encounter in Journey Builder When Creating New Versions
Journey Builder is a dynamic tool, and as with any technology, updates and new versions are common. In this section, we’ll explore potential issues that you might encounter when creating new versions of your customer journeys.
Being aware of these challenges can help you proactively address them, ensuring a seamless transition to the latest Journey Builder version.
Common Challenges in Journey Builder Version Updates
- Compatibility issues with existing journey configurations
- Changes in data extension requirements
- Impact on existing customer journeys and their performance
Each of these may require manual quality assurance upon every update – testing, diagnosing, and remedying.
Setting a Data-Driven Course: Your Journey Begins Here
As we conclude this comprehensive guide, we hope you’ve gained valuable insights into preparing your data for seamless integration with Salesforce Journey Builder. It’s been a journey, exploring the critical foundations of data storage, mastering data taxonomy, and unlocking the potential of Journey Builder.
Now, let’s take a moment to pause and look back at the journey you’ve embarked upon. In this concluding section, we’ll bring together the essential lessons, strengthen your grasp of best practices, and ensure every one of your data-driven marketing campaign launch can set off with confidence.
In the opening chapters, we emphasized the significance of optimal data storage. You learned how proper data management is the bedrock of any successful marketing campaign. Remember, maintaining clean, well-organized data leads to streamlined processes and insightful decision-making.
Taxonomy: The Art of Organization
Our journey through data taxonomy revealed the art of structuring your data. By creating a robust framework, you set the stage for data that’s easy to retrieve, analyze, and activate. The use of naming conventions, metadata, and categorization helps your data become a powerful asset.
Journey Builder Integration
As we ventured into the realm of Journey Builder, you discovered how this tool can propel your marketing efforts to new heights. The importance of data mapping, formatting, and thorough testing cannot be overstated. These are the pillars that uphold your data’s success in Journey Builder. Keep in mind that Journey Builder does not work with Lists.
Best Practices for Data Governance
Data governance and documentation are not the final destination but rather a continuous process. Establishing protocols and routines for data management are key to maintaining the quality and security of your data.
Continuous Evolution
The world of data never remains static. It’s ever evolving, much like your customers’ needs and expectations. Ensure that your data strategies are scalable and future-proof, allowing you to adapt and grow as your data requirements change.
Your Data-Driven Journey Awaits
It’s important to remember that the road ahead has hurdles. You might encounter challenges, but armed with the knowledge you’ve gained, you’re more than equipped to navigate them. Whether you’re a seasoned marketer with years of experience under your belt or someone just beginning to explore the possibilities, always keep in mind that data is not an adversary but a trusted ally by your side.
Your success lies in your commitment to data excellence, from storage to integration, and beyond. It’s a journey where data becomes a powerful asset, and Journey Builder becomes your canvas for crafting remarkable customer experiences.
So, what’s next for you? It’s time to put theory into practice, to experiment and explore. Your journey begins here. Take those insights, experiment, and make data your trusted companion in your marketing endeavors.
Thank you for joining us on this data-driven expedition. Safe travels, and may your path be paved with data-driven success.
DESelect makes it easy to standardize how your team uses SFMC for maximum efficiency. Learn how marketers instantly find any object in Marketing Cloud with DESelect Search – free on the AppExchange!
Table of Contents

William McMahon
CEO & Founder at Gravitai, William has over 15 years experience in the CRM world as both a top UK Salesforce Partner and Ex-ExactTarget Principal Solutions Architect.

Salesforce Marketing Cloud is a powerful platform that enables marketers to create, manage, and execute campaigns across multiple channels.
As industries forever evolve, it has become imperative for organizations to stay agile and not fragile.
Growth, expansion, restructuring, and so many other factors often create the need for organizations to share data across various business units.
Today I invite you to join me as we explore the data-sharing capabilities SFMC offers and ways to counter the potential challenges that often come with sharing data.
But first, we need to understand the key data elements of SFMC, including how large organizations operate through business units and how they store their data.
Part 1: The What
Business Units
Many enterprise organizations, especially those with many brands under one umbrella, will operate with multiple business units under a parent account. Each is a separate Marketing Cloud environment with its own set of assets, users, and data.
By default, each business unit operates in a silo and cannot access data or assets from other business units.
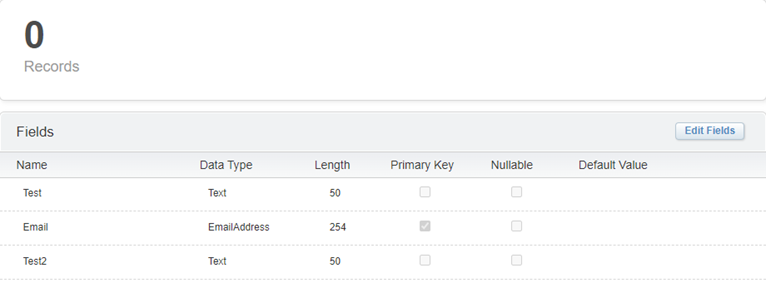
Data Extensions
A data extension is a table-like structure used for data storage within SFMC. Unlike a static list, data extensions offer the ability to create more personalized and constantly updating data to suit organizational requirements.
You can use data extensions to store different data types, such as text-, number-, and date-based records; boolean (true/false statements), email addresses, and more. This data is used to create accurate and relevant marketing campaigns that target a subscriber base.
Audiences
Audiences are groups of subscribers (Contacts) used during campaigns. Audiences in SFMC can be created by combining various data sources such as customer purchase history, customer engagement, and demographic information.
Data gathered on audiences can be used to personalize communications. For example, targeting subscribers in a certain country with localized offers will drive better engagement rates than general mass marketing.
Publication List
A Publication list is a list of contacts/subscribers who have opted in to receive specific communication from your organization, such as a Monthly Newsletter. Amid tight GDPR regulations, maintaining robust publication lists becomes essential to today’s marketing teams reliant on explicit subscriber consent.
Part 2: The How
Now let’s look at the various ways to share data within SFMC.
Shared Data Extensions
Shared data extensions can be created in one business unit and shared with other business units. This allows for quick, painless sharing of data across various business units.
Shared Audiences
An audience can be created in one business unit and shared across others, enabling all business units to target the same contacts.
Shared Data Sources
Data sources are external applications or databases which can be connected to SFMC. For example, addingSalesforce CRM as a data source connects that data to all Marketing Cloud business units.
Shared Publication List
A shared publication list can be accessed and used by multiple business units or accounts within your organization.
Part 3: The Why: Best Practices for Sharing Data Across Business Units
When planning your data strategy, carefully map what data needs to be shared, with whom, and how this will be shared. Consider the following.
- Shared Data Extensions: While these are powerful means of sharing record data, sharing data extensions across business units require proper management. Primary items to consider would be:
- Naming Conventions – Create a naming standard which can be used across all business units. This makes it easier for teams to search for and quickly find requested data.
- Data Structure – Utilize a data blueprint which can be shared with all relevant stakeholders. Mapping out nested data ensures ease-of-access for both marketers and admins.
- Data Map – Have admins determine how mapped data fields and objects with relationships can be used for segmentation at each business unit.
- Sharing Permissions: SFMC allows you to define granular permissions for sharing data across business units. Define roles and permissions carefully and ensure that users only have access to the data they need. This prevents errors from inexperienced users and protects customer data from improper use.
- Shared Audiences: Sharing audiences across business units allows for quick data share but does need alignment with Marketing/Campaign strategies. This requires management to ensure that audience data is utilized correctly. For example, if we have an audience that all business units share and market to, then without a group strategy, this audience may get flooded with communication.
- Monitor your Sharing Strategy: Monitor your data sharing across all business units to ensure users adhere to your sharing strategy. A few key points for a monitoring strategy:
- Users should only have access to the data they need.
- Campaign/Marketing Strategies should be aligned to ensure that contacts are not oversaturated.
- Maintain a data blueprint and ensure your landscape is mapped.
- Frequently review your user permissions and sharing rules.
- Sharing Frequency: Data sharing can occur on four primary frequencies:
- Real-time – data is synced as soon as an update occurs.
- Daily – data is synced once a day.
- Weekly – data is synced once a week.
- Monthly – data is synced once a month.
As part of your sharing strategy, it is imperative to align your shared data to the correct frequency, e.g., we do not need to update a data extension on a real time basis if it only receives data once a week.
Ensure that your frequency caters for the needs of your organization and is aligned with the type of data you are sharing.
Conclusion
Sharing data across business units offers a powerful way to streamline marketing, increase efficiency, and ensure users have access to the data they need.It is, however, extremely necessary to ensure that you have a proper sharing strategy, and that sensitive information is fully protected.

Jay Slinger
Jay is a Technical Architect with over two decades of industry experience. He has worked with several fortune 500 companies and spearheaded many multi-million projects.

Storing subscriber data in Salesforce Marketing Cloud can be trickier than most marketers expect. As a versatile and powerful tool, SFMC offers more than one way to store subscriber lists or data within data extensions. This article intends to help you determine the best method for storing your data in the Marketing Cloud.
What kind of data can be stored?
Just about anything! Purchases, accounts, orders, types of products, and even personal data such as birthdays, email addresses, etc. These specific pieces of information can be combined to craft highly personalized points of communication, ensuring optimal customer engagement. While Marketing Cloud can be much more than just a data warehouse, its storage capabilities should not be overlooked for your future marketing campaigns.
Before looking for data storage solutions, marketers should first define which type of data model their marketing campaigns and operations require: 1-to-1 or 1-to-many. For example, if there is one email address and one Subscriber ID that relates to this email, it’s 1-to-1. On the other hand, if there is the need to relate this Subscriber ID to the purchase information, it would be 1-to-many, given that one subscriber can make several purchases.
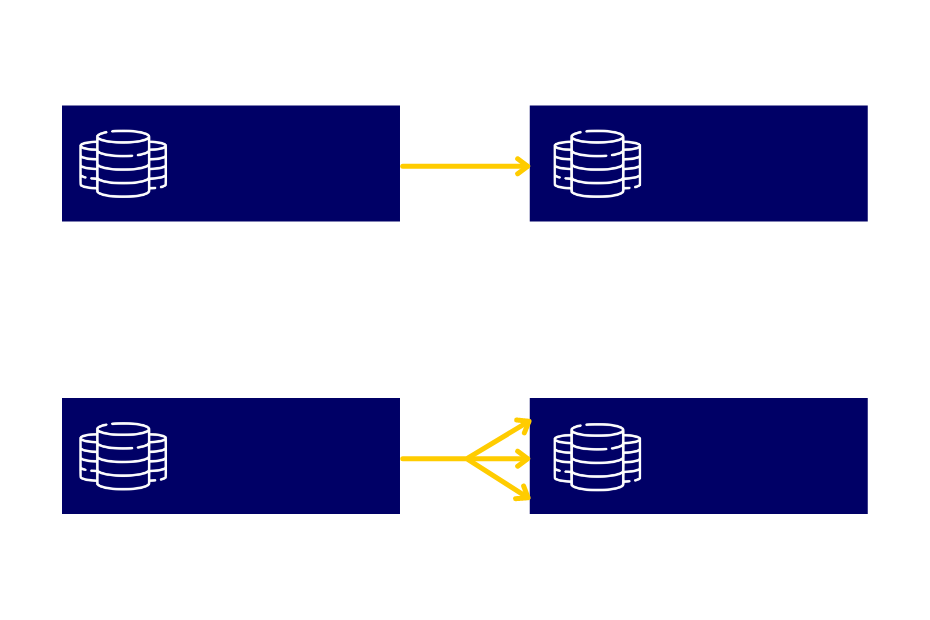
However, it might be the case that the subscriber information relates to their other activities, further increasing the complexity of the 1-to-many data model. This would require a more flexible way to store that data so that it can be manipulated later.
Understanding Salesforce lists
Lists are the most basic way to store your subscribers’ data in SFMC. They are most useful when:
- Working with 1-to-1 data models
- The number of subscribers is below 500,000, and
- Customer segmentation needs are of low complexity.
In the case of a more extensive list of subscribers or a more complicated data model, businesses should opt for data extensions (DEs) for closer control over their marketing practices.
What are Salesforce data extensions?
Data extensions allow for more flexibility when it comes to data management and are the preferred method for dealing with 1-to-many data models. In simple terms, DEs are tables capable of containing a greater multitude of data than Salesforce lists.
Usually, they are utilized for storing data above 500,000 rows. They are also frequently used to import and store data from other systems through Marketing Cloud Connect (to send data from Salesforce Core to Salesforce Marketing Cloud) and similar tools.
Due to the variety of the types of information they can hold, DEs can be used for both transactional and commercial communication.
Data extensions also grant additional control over segmentation, although their setup can be more time-consuming than lists. Salesforce Marketing Cloud possesses built-in filters for simple requests, while more advanced segmentation requirements call for SQL queries. Tools such as DESelect Segment can help marketing teams work around the inconvenient and time-consuming task of SQL writing. This user-friendly app, available as a Chrome Extension and in the Appexchange, allows marketers to enjoy all the powerful functionalities of SQL queries while eliminating the need to write even a single line of code.
What is the difference between lists and data extensions?
Lists are only able to store basic subscriber data, such as email address, first name, last name, and so on, using the standard profile and subscription center. Alternatively, Data Extensions have minimal rules when it comes to storing data – they can be set up in whichever way best fits your org’s needs.
It is worth noting that setting up DEs may take some time, given that users should know what type of data is added to which field and follow a previously defined naming pattern (otherwise it becomes difficult to use the data when it comes to segmentation, for example). Data extensions do not require an email address (unlike lists) and can also store more advanced data such as product catalogs, sales representative information, and even behavioral data such as abandoned carts and site interactions.
When it comes to segmentation best practices, data extensions are preferred for 1-to-many data models. Critically, they allow marketers the option to create granular segments of their audiences through SQL queries, a process not possible with lists. In order to segment their audiences using lists, marketers would need to take the time to create several different lists.
In short, lists are best used for specific email sends lacking advanced data, whereas data extensions can be used for basically any type of communication or data management need. If the goal is to organize data with simplicity, go for lists. If you require fast import speed and support multiple subscriber datasets, use data extensions.
Conclusion
Using data extensions in Salesforce Marketing Cloud has many benefits for companies that store large quantities of data.
It is recommended to define the specific needs of your data model in advance and to determine how it will be stored in SFMC, as this will determine when and where to best use lists and/or data extensions. Also, keep in mind that Marketing Cloud is not a data warehouse, so there is no need to add all your data there just because you can.
One of the main advantages of using DEs in Marketing Cloud is data segmentation. Marketers can rely on SQL (if they have the technical knowledge), use filters for simple segmentation requests, or take advantage of a drag-and-drop alternative like DESelect Segment to make the process quick and intuitive for everyone.
- What data are we talking about?
- What are Salesforce lists?
- What are Salesforce data extensions?
- What is the difference between lists and data extensions?
- Conclusion
Latest Articles
-
Company Culture Meet Our Team: Creative & Web Manager, Kyra Constam In the dynamic world of design, Kyra Constam stands as a definition of talent and innovation. Get her take on her DESelect journey → Her journey at DESelect began with the title of Senior Graphic Designer, where her talent and hard work shined […]March 27, 2024While Salesforce’s Marketing Cloud has long been synonymous with cutting-edge marketing automation, the unveiling of Marketing Cloud Growth Edition (MCG) marks a pivotal moment in democratizing marketing prowess. It is the very first glance of a marketing app developed in-line with Salesforce’s core platform and what it embodies. It is a big announcement from Salesforce […]March 26, 2024In the dynamic and competitive realm of B2C marketing, understanding the stages of the customer journey is essential for crafting compelling marketing strategies that resonate with consumers at every touchpoint. This journey, a detailed map of a consumer’s engagement with a brand, is pivotal in shaping customer experiences and driving conversions. Let’s embark on a […]March 21, 2024You’ve already mastered segmentation in your everyday life. Your relationship with your family, friends, and colleagues is the biggest proof of your mastery. Why? Because you know what everyone around you likes and dislikes. And you tailor to their segment their behaviors, needs, lifestyles, and hobbies to keep them happy. If your best friend is […]March 20, 2024

How to personalize your marketing campaigns with data in Salesforce Marketing Cloud?
A survey created by Think with Google mentions that 90% of marketers think that marketing personalization significantly contributes to business profitability. Yet still, 58% of consumers say brands send them items that they don’t want. When it comes to personalization, it takes time to recognize the problem and act upon solving it. The question that marketers can ask themselves is where to start? And our answer will always be — start with data. Let’s find out how to leverage big data for personalization at scale and be ahead of the game.
First, define what data you need to collect. There are all sorts of data out there that your company probably already collects. You most likely track the data about your website visitors, collect data about your customers, store their personal information in your CRM, and probably create email marketing campaigns where the engagement of your subscribers is monitored. If you do all of that, that’s a great start, but how to use all that big data for personalization in Marketing Cloud? That’s something you’re about to find out now.
Focus on different aspects of data
Guillaume Cabane, former VP of Growth at Drift and Segment, recommends using data to enrich your marketing personalization strategy and confirm visitors’ information to create a frictionless experience. However, not all data you collect from visitors and customers is actionable.
To generalize, we can put data into two categories: quantitative and qualitative. Under quantitative the following types of data can be found:
- Demographic data – a collection of all the data points about a person, such as their name, email, title, income, location, marital status, and more.
- Firmographic data – a collection of all the data points about a business, such as company name, industry, number of employees, annual revenue, and stage in the sales cycle.
- Behavioral data – in the context of interaction between a website user and an app user, this reveals the data collected from your website or app visitors, such as pages visited, links clicked, average time on site, and a count of visits.
- Contextual data – collection of data related to a visitor’s unique properties while providing context to their behavior on a website or an app, such as device type, browser type, location, and time of the day. Collecting demographic and firmographic data requires your visitors to fill out and submit a form. This may include a newsletter subscription, a demo registration, a live chat transaction, or a lead magnet download. This data typically ends up in your CRM, where you also get some automatic date and time stamping, lead source tracking, and lead activity insights.
Qualitative data, on the other hand, can be collected via questionnaire-style scenarios so that the customer’s attitudes, motivations, and opinions are collected. Some of the information that can be collected includes:
- Opinion (e.g., their favorite journey destination for a holiday)
- Motivations (why service was requested)
- Attitudinal information (e.g., customer satisfaction reviews)
All the data you collect falls into one of these boxes. Later, you need to enable the process that allows creating a single view of a customer. Marketers tend to use CRM to access customers’ information. However, since data comes from different sources, it’s more common to operate between multiple platforms, which complicates the process of managing data and using it for later personalization. Ideally, all data points should connect and create a 360 view of a customer to tailor the communication based on their individual needs and position in the purchase cycle.
Another way to store and create a 360 view of an individual is to acquire a CDP (Customer Data Platform), which aims to create a single customer view. This solution can be convenient for those professionals who receive ample amounts of data and want to manage it outside of Salesforce Marketing Cloud. Recently, Salesforce announced their CDP. Read our What is CDP article to find out more about Customer Data Platforms.
Connect data dots
Different data types come from various sources, but how would you know which ones to focus on? Or which one is the most valuable? Here’s a quick overview of different data sources SFMC marketers need to take into consideration.
First-party data
First-party data is the relevant information that your company gets from your customers, prospects, and subscribers. It’s essential to have this information since it enables you to identify individual customers and deliver highly relevant experiences. Common first-party data sources are:
- Data collated from native app or website behavior
- Data from your CRM
- Social data
- Subscription data
- Behavioral data
- Purchase data
- Attitudinal data
Second-party data
Second-party data is like first-party data, but it comes from a source other than your own. It’s first-party data for other entities. Its value lies in its scale, as it can be pretty expansive, allowing for more data analytics insights on customer behaviors, new audiences, and relationship-building exercises. Second-party data sources are:
- Social media
- Customer surveys
- Activity on websites
- In-store purchase information
Third-party data
Third-party data is usually what entities acquire from external sources, where the sources are not the original owners of that data. These sources collect data and sort them together to sell them to potential clients. It is also not 100% consensual data, which makes it less reliable and likely to use. Examples can be:
- Demographic data
- Interests
- Firmographic data
- Website activity
Looking at different data sources, first-party data is the most important, reliable, and valuable data for any business. Second and third-party data can fill in the gaps but are not always relevant or valuable. Usually, small and mid-size companies benefit from purchasing third-party data when their first-party data pool is relatively limited. In the end, your first-party data is all about your customers or prospects, and that’s the group that you need to focus on.
That is why it’s so important to scale your first-party data and make the best use out of it. To do this, marketers need to have data in one place, and what place can be better than Salesforce Marketing Cloud? Nonetheless, it’s not that easy for marketers to leverage big data that ends up in the Marketing Cloud. Firstly, marketers need to inject data coming from Salesforce CRM or other acquisition sources. Indeed, tools like Marketing Cloud Connect are there to connect Salesforce CRM with Marketing Cloud; however, it’s quite a technical thing to do for a non-data-savvy marketer. You can rely on external help like an IT team in your company or system integrators to do this for you. That’s because it requires understanding the data model and knowing how to build the connection. In general, it can be considered a separate project that, if not asking for external help, can take up a lot of marketing time. As a result, the time that marketers can spend on the actual campaign creation and building customer journeys will be absorbed by establishing the connectors between Salesforce CRM and Salesforce Marketing Cloud.
Declutter your data for better marketing personalization
The secret to using big data effectively is identifying which metrics are relevant to your audience, disregarding the rest. Such focus allows you to develop and execute campaigns quickly that address your users’ needs.
Remember that not all data you collect needs to be used or stored in Salesforce Marketing Cloud since it’s not a data warehouse. Ensure that you ingest only the data that can be used to create meaningful communication with your subscribers, customers, and prospects. There’s a steep learning curve to doing marketing personalization right; mastering it requires time, patience, and interdepartmental collaboration.
Then you can move on to segmenting your data. Marketers’ work doesn’t stop with just identifying your core customers. You need to segment your audience into smaller groups for more accurate targeting. How? One way to do that is to go through the available data to find repeating patterns in behavior or user engagement across different touchpoints. Then, divide your audience into segmented groups based on which pattern they represent. This will help you personalize your campaigns more effectively. There are different types of market segmentation and it’s important you have a clear understanding of segmentation strategies, that can help you better segment your audience in Salesforce Marketing Cloud for highly targeted campaigns.
It’s worth mentioning that segmenting data in the Salesforce Marketing Cloud requires learning SQL query language. Marketers either need to have SQL knowledge or rely on their colleagues with better data management capabilities or third-party service providers to create segments. Fortunately, there is an alternative for marketers working with SFMC who want to segment efficiently and independently without writing a single line of code. This is an intuitive no-code segmentation solution called DESelect Segment that creates advanced audience segments in Marketing Cloud easy to use for personalization later. Schedule a live demo with one of DESelect certified consultants already now to improve your segmentation game.
Let’s start personalizing in Marketing Cloud
Now you have all the data you need in one place — Salesforce Marketing Cloud, and you’ve created your segments; well done, you made it! Now it’s about time to personalize it.
Real-time personalization with Interaction Studio
On-site personalization has become a buzzword in the marketing world, and that can be partially attributed to the existence of Interaction Studio in Salesforce Marketing Cloud. You can leverage this tool to create live, personalized experiences for your website visitors. Based on the segments you created earlier, you can tailor your website visitors’ experience using the insights of their needs and interests to personalize the communication and create a 1-to-1 relationship with every customer and prospect visiting your website.
Interaction Studio overview example (source: https://www.salesforce.com/eu/products/marketing-cloud/customer-interaction/)
Leverage AI insights for better customer experience
A great method to create advanced personalization on the go can be incorporating AI mechanisms like Einstein Recommendations in Salesforce Marketing Cloud. These recommendations allow you to create personalized suggestions enabled by AI to deliver the best-personalized results for every customer by creating customer profiles for your audience. To leverage Einstein Recommendations for Marketing Cloud, you need to understand some underlying and somewhat technical aspects that come along. You can have an overview of what Einstein Recommendations are in this Trailhead module. Einstein features are accessible for Salesforce Marketing Cloud clients starting from the Corporate tier.
Learn AMPscript and optimize your email marketing
Another option to create personalized experiences for your Salesforce Marketing Cloud audience is to leverage AMPscript. This is another language that technical marketers use in SFMC to create personalized experiences in Email Studio. However, this may mean that you need to invest in learning how to code. Leveraging this language can help you automate certain marketing activities like cleaning and formatting data and personalize emails based on subscriber and contact data. It’s good to become familiar with the AMPscript basics, which you can find in this helpful Trailhead module. Getting acquainted with it will be an asset to understand the best way to personalize your communication with your audience.

AMPscript example (source: Trailhead)
Deliver personalized experiences with Journey Builder
Journey Builder is truly a multipurpose tool that can help you build advanced journeys and meaningful 1-to-1 connections with your audience. For instance, you can insert audience segments you created with DESelect Segment in the journey’s starting point and create a tailored experience that will be valuable specifically for this segment. Based on website activity, interaction with the emails, purchases, and leaving feedback, you can deliver a personalized experience to every contact.
Conclusion
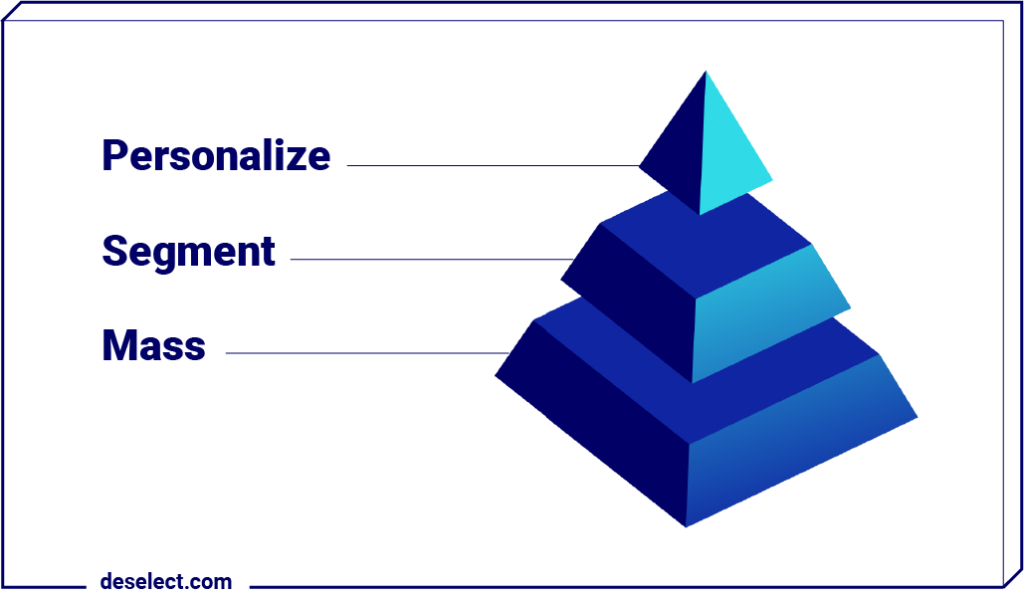
There are many ways to personalize your marketing campaigns and communication with your customers or prospects in Salesforce Marketing Cloud, but that is first and foremost dependent on getting your data right and knowing how to use it. According to the Salesforce 7th State of Marketing Report, 78% of marketers say their customer engagement is data-driven. There’s no personalization without knowing the data you have and how to use it to your benefit. You have to start leveraging Marketing Cloud to where all data-puzzle pieces come together in order to be able to start segmenting your audience. Thanks to SFMC solutions like DESelect Segment that becomes easy and accessible to all marketers. After that, when your segments are defined, you can personalize your communication and create highly personalized journeys that will speak to every individual and build trust between you and your customers. Good luck!
- How to personalize your marketing campaigns with data in Salesforce Marketing Cloud?
- Focus on different aspects of data
- Connect data dots
- Declutter your data for better marketing personalization
- Let’s start personalizing in Marketing Cloud
- Conclusion
Latest Articles
-
Kyra Constam, Creative & Web Manager
Company Culture Meet Our Team: Creative & Web Manager, Kyra Constam In the dynamic world of design, Kyra Constam stands as a definition of talent and innovation. Get her take on her DESelect journey → Her journey at DESelect began with the title of Senior Graphic Designer, where her talent and hard work shined […]March 27, 2024Salesforce Announce Marketing Cloud Growth Edition Built on Top of Data Cloud
While Salesforce’s Marketing Cloud has long been synonymous with cutting-edge marketing automation, the unveiling of Marketing Cloud Growth Edition (MCG) marks a pivotal moment in democratizing marketing prowess. It is the very first glance of a marketing app developed in-line with Salesforce’s core platform and what it embodies. It is a big announcement from Salesforce […]March 26, 2024What Are the Typical Stages of the B2C Customer Journey?
In the dynamic and competitive realm of B2C marketing, understanding the stages of the customer journey is essential for crafting compelling marketing strategies that resonate with consumers at every touchpoint. This journey, a detailed map of a consumer’s engagement with a brand, is pivotal in shaping customer experiences and driving conversions. Let’s embark on a […]March 21, 2024Segmentation in Salesforce Marketing Cloud (SFMC)
You’ve already mastered segmentation in your everyday life. Your relationship with your family, friends, and colleagues is the biggest proof of your mastery. Why? Because you know what everyone around you likes and dislikes. And you tailor to their segment their behaviors, needs, lifestyles, and hobbies to keep them happy. If your best friend is […]March 20, 2024Join our newsletter to receive updates and helpful SFMC guides.
Report: 2024 State of AI & Personalization in Marketing
Discover how your peers across the globe are planning to adopt AI and Personalization for marketing strategies they will pursue in 2024.
We surveyed over 300 marketers across five continents to get a pulse of how marketing teams plan to use AI and advanced personalization in their campaigns over the coming year.
With over 50 pages of insights, we delve into how marketing teams plan to augment the human side of campaign generation with tools that automate or drive more resonant customer experiences.
Some of the highlights of our report:
- Marketers overwhelmingly support using AI in their jobs
- Teams are expanding how they use AI and personalization to more effectively run campaigns
- Those who invest in these technologies tend to see satisfactory results
Download now to get the full scoop!

Guide: 32 Industry-Specific Email Marketing Templates from ChatGPT
We tested how well ChatGPT could craft common email campaigns for nine industries. While this AI provides some very useful templates for email marketers to mold, we found it ultimately needs a human touch to get just right. However, this isn’t the entire story.
Rather than replace marketers, knowing what types of questions to ask ChatGPT enhances the marketing experience with quick, modifiable email copy that lays the groundwork for engagement and clicks.
Industries covered:
- Insurance
- Retail and eCommerce
- Banking
- Automotive
- Nonprofit
- Hospitality and Leisure
- Telecom
- Media and Publishing
- B2B and SaaS
Download the free guide!

eBook: Data driven personalization
Get your copy of our eBook and find out how you can improve customer experience with personalized data in Salesforce Marketing Cloud
We’ve been collecting data for years, and while more recently, there’ve been considerable advances in data science and marketing, we still continue to gather data en masse, often because “we can.” The truth is that companies collect too much data. 18% of companies are using 20 or more data sources for decision-making. Our survey results indicate that this figure will grow in the future. The questions to consider here are why are we collecting the data we collect? Have we truly defined its purpose, or is it a “just in case” scenario? Or do we simply not know?
Organize your Salesforce Marketing Cloud to improve your ROI
According to the Salesforce State of Marketing Report (7th Edition), marketers expect a 40% increase in the number of data sources they use between 2021 and 2022. This is a whopping increase that will bring new challenges to companies' data strategy. It will also naturally lead to companies holding inconsistent data problems with data governance and management that may well result in security breaches.
Pro tip: Count the data sources your company is collecting. We guess it's more than 20. Then take a moment to ask three fundamental questions:
- Do you utilize this data to its full potential?
- What is your goal in collecting all of this data?
- Are you satisfied with the state of your data collection at this point in time?
If you can quickly answer all these questions, you might not need this book, but if these questions resonate with your own doubts and concerns, we invite you to read further — we'll try to find a solution together.
Types of data you need to collect
Perhaps we should start by breaking down types of data into basics. In general terms, we can put data into two categories: quantitative and qualitative.
Quantitative data
Under the classification of quantitative data, the following types of data can be found:
Demographic data – a collection of all the data points about a person, such as their name, email, title, income, location, marital status, and more.
Firmographic data – a collection of all the data points about a business (a 'firm'), such as company name, industry, number of employees, annual revenue, and stage in the sales cycle.
Behavioral data – data on the interaction between website users and app users. This reveals the data collected from your website or app visitors, such as pages visited, links clicked, average time on site, and a count of visits, retention rate, churn rate, daily & monthly active use, and more.
Contextual data – data related to a visitor's unique properties while providing context to their behavior on a website or an app, such as device type, browser type, location, and time of the day.
Collecting demographic and firmographic data requires your visitors to fill out and submit a form. This may include a newsletter subscription, a demo registration, a live chat transaction, or a lead magnet download. This data typically ends up in your CRM, where you also obtain some automatic date and time stamping, lead source tracking, and lead activity insights.
Qualitative data
On the other hand, qualitative data can be collected through questionnaire-style methods to garner the customer's attitudes, motivations, and opinions. Some of the qualitative information that can be collected includes:
Opinion (e.g., their favorite journey destination for a holiday).
Motivations (why they requested a particular service).
Attitudinal (e.g., customer satisfaction reviews).
All the data you collect falls into one of these boxes. Later, and as you'll see, you need to design a process that allows you to create a single customer view.
Data you need to improve personalization
It'll come as no newsflash to you to hear that personalization is the key to successful data marketing. And with so many incredible sales & marketing automation tools at our disposal, there are myriad ways for us to interact with customers (and potential customers) in creative and engaging ways.
80% of consumers are more likely to purchase from a brand that provides personalized experiences.
— Epsilon
-
All data you collect - why do you need it and what to do with it?
-
Segmentation using the data you gather
-
What about cookies?
-
Getting to know the customer in a non-intrusive way
Personalize customer experience in SFMC with data.
Sign up to get your free eBook now.